Genomic characterization of Wilms' tumor suppressor 1 targets in nephron progenitor cells during kidney development
- PMID: 20215353
- PMCID: PMC2835332
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.045732
Genomic characterization of Wilms' tumor suppressor 1 targets in nephron progenitor cells during kidney development
Abstract
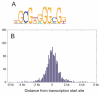
The Wilms' tumor suppressor 1 (WT1) gene encodes a DNA- and RNA-binding protein that plays an essential role in nephron progenitor differentiation during renal development. To identify WT1 target genes that might regulate nephron progenitor differentiation in vivo, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) coupled to mouse promoter microarray (ChIP-chip) using chromatin prepared from embryonic mouse kidney tissue. We identified 1663 genes bound by WT1, 86% of which contain a previously identified, conserved, high-affinity WT1 binding site. To investigate functional interactions between WT1 and candidate target genes in nephron progenitors, we used a novel, modified WT1 morpholino loss-of-function model in embryonic mouse kidney explants to knock down WT1 expression in nephron progenitors ex vivo. Low doses of WT1 morpholino resulted in reduced WT1 target gene expression specifically in nephron progenitors, whereas high doses of WT1 morpholino arrested kidney explant development and were associated with increased nephron progenitor cell apoptosis, reminiscent of the phenotype observed in Wt1(-/-) embryos. Collectively, our results provide a comprehensive description of endogenous WT1 target genes in nephron progenitor cells in vivo, as well as insights into the transcriptional signaling networks controlled by WT1 that might direct nephron progenitor fate during renal development.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The transcription factor Sry-related HMG box-4 (SOX4) is required for normal renal development in vivo.Dev Dyn. 2013 Jun;242(6):790-9. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.23971. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Dev Dyn. 2013. PMID: 23559562
-
WT1 and kidney progenitor cells.Organogenesis. 2010 Apr-Jun;6(2):61-70. doi: 10.4161/org.6.2.11928. Organogenesis. 2010. PMID: 20885852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of an siRNA-based method for repressing specific genes in renal organ culture and its use to show that the Wt1 tumour suppressor is required for nephron differentiation.Hum Mol Genet. 2004 Jan 15;13(2):235-46. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddh015. Epub 2003 Nov 25. Hum Mol Genet. 2004. PMID: 14645201
-
WT1 targets Gas1 to maintain nephron progenitor cells by modulating FGF signals.Development. 2015 Apr 1;142(7):1254-66. doi: 10.1242/dev.119735. Development. 2015. PMID: 25804736 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic States of nephron progenitors and epithelial differentiation.J Cell Biochem. 2015 Jun;116(6):893-902. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25048. J Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25560433 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic transcriptional reprogramming by WT1 mediates a repair response during podocyte injury.Sci Adv. 2020 Jul 24;6(30):eabb5460. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb5460. eCollection 2020 Jul. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32754639 Free PMC article.
-
EED, a member of the polycomb group, is required for nephron differentiation and the maintenance of nephron progenitor cells.Development. 2018 Jul 18;145(14):dev157149. doi: 10.1242/dev.157149. Development. 2018. PMID: 29945864 Free PMC article.
-
Wilms tumor protein-dependent transcription of VEGF receptor 2 and hypoxia regulate expression of the testis-promoting gene Sox9 in murine embryonic gonads.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 8;292(49):20281-20291. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.816751. Epub 2017 Oct 17. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29042436 Free PMC article.
-
Wt1a, Foxc1a, and the Notch mediator Rbpj physically interact and regulate the formation of podocytes in zebrafish.Dev Biol. 2011 Oct 15;358(2):318-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.08.005. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21871448 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid screening of gene function by systemic delivery of morpholino oligonucleotides to live mouse embryos.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 28;10(1):e0114932. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114932. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25629157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ai X., Kitazawa, T., Do, A. T., Kusche-Gullberg, M., Labosky, P. A. and Emerson, C. P., Jr (2007). SULF1 and SULF2 regulate heparan sulfate-mediated GDNF signaling for esophageal innervation. Development 134, 3327-3338. - PubMed
-
- Alcedo J., Ayzenzon, M., Von Ohlen, T., Noll, M. and Hooper, J. E. (1996). The Drosophila smoothened gene encodes a seven-pass membrane protein, a putative receptor for the hedgehog signal. Cell 86, 221-232. - PubMed
-
- Andersson T., Sodersten, E., Duckworth, J. K., Cascante, A., Fritz, N., Sacchetti, P., Cervenka, I., Bryja, V. and Hermanson, O. (2009). CXXC5 is a novel BMP4-regulated modulator of Wnt signaling in neural stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 3672-3681. - PubMed
-
- Arnaud L., Ballif, B. A., Forster, E. and Cooper, J. A. (2003). Fyn tyrosine kinase is a critical regulator of disabled-1 during brain development. Curr. Biol. 13, 9-17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

