Uric acid does not affect the acetylcholine-induced relaxation of aorta from normotensive and deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive rats
- PMID: 20215410
- PMCID: PMC2879926
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.109.160184
Uric acid does not affect the acetylcholine-induced relaxation of aorta from normotensive and deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive rats
Abstract
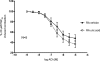
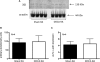
Uric acid (UA) results from xanthine oxidase (XO) catabolism of xanthine and is the final product of purine catabolism in humans. In this species, hyperuricemia is associated with gout, nephropathy, and increased cardiovascular disease risk. Although the effects of hyperuricemia in vascular biology are overall controversial, UA has been described as an antioxidant and as potentially improving endothelial function. Hypertension is associated with endothelial dysfunction. We hypothesized that UA improves the endothelial function of aorta from deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA)-salt hypertensive rats. UA (100 microM) in the presence of the uricase inhibitor oxonic acid (10 microM) did not modify relaxation to acetylcholine (ACh) (1 nM-10 microM) in the aorta from nontreated, sham normotensive, and DOCA-salt hypertensive rats [response to 10 microM ACh for UA versus vehicle, respectively: nontreated = 37 +/- 7 versus 48 +/- 7%, sham = 53 +/- 15 versus 57 +/- 20%, DOCA = 81 +/- 4 versus 85 +/- 2% from 20 microM prostaglandin 2alpha (PGF(2alpha))-induced contraction]. Allopurinol (100 microM), a XO inhibitor, did not significantly alter the ACh-induced relaxation of sham and DOCA aortic rings (response to 10 microM ACh for allopurinol versus vehicle, respectively: sham = 61 +/- 5 versus 68 +/- 9%, DOCA = 87 +/- 6 versus 88 +/- 3% from 20 microM PGF(2alpha)-induced contraction). Uricemia, ranging from unmeasurable to 547 microM in sham and to 506 microM in DOCA rats, was not significantly different between these two groups. The expression and activity of XO, as well as the expression of uricase, were not different between sham and DOCA rat aorta. We conclude that, at least in vitro, UA does not affect the ACh-induced relaxation of normotensive and DOCA-salt hypertensive rats.
Figures
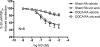
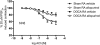

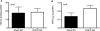

Similar articles
-
Role of oxidative stress and nitric oxide in regulation of spontaneous tone in aorta of DOCA-salt hypertensive rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Feb;141(4):562-73. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705557. Epub 2004 Jan 26. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 14744820 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of enalapril on the endothelial function of DOCA-salt hypertensive rats.Gen Pharmacol. 2000 Feb;34(2):117-25. doi: 10.1016/s0306-3623(00)00053-7. Gen Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10974419
-
Influence of endothelium on Mg(2+)-induced relaxation in noradrenaline-contracted aorta from DOCA-salt hypertensive rat.Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jun 13;258(3):167-72. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90477-4. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 8088352
-
Endothelin-1-induced contraction in isolated aortae from normotensive and DOCA-salt hypertensive rats: effect of magnesium.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Dec;119(7):1367-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb16048.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8968545 Free PMC article.
-
Xanthine oxidase and mitochondria contribute to vascular superoxide anion generation in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Jul;295(1):H281-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00304.2008. Epub 2008 May 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18487445 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Male and female high-fat diet-fed Dahl SS rats are largely protected from vascular dysfunctions: PVAT contributions reveal sex differences.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021 Jul 1;321(1):H15-H28. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00131.2021. Epub 2021 Apr 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33929898 Free PMC article.
-
Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate-induced contraction is increased in renal but not pulmonary arteries from DOCA-salt hypertensive rats.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Aug;301(2):H409-17. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00084.2011. Epub 2011 May 6. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21551273 Free PMC article.
-
The role of uridine adenosine tetraphosphate in the vascular system.Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2011;2011:435132. doi: 10.1155/2011/435132. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22110488 Free PMC article.
-
Defensive effect of natrium diethyldithiocarbamate trihydrate (NDDCT) and lisinopril in DOCA-salt hypertension-induced vascular dementia in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 Oct;223(3):307-17. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2718-9. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22526544
-
Serum Uric Acid as an Independent Risk Factor for the Presence and Severity of Early-Onset Coronary Artery Disease: A Case-Control Study.Dis Markers. 2018 Oct 23;2018:1236837. doi: 10.1155/2018/1236837. eCollection 2018. Dis Markers. 2018. PMID: 30425752 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becker BF. (1993) Towards the physiological function of uric acid. Free Radic Biol Med 14:615–631 - PubMed
-
- Beckman JS, Koppenol WH. (1996) Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: the good, the bad, and ugly. Am J Physiol 271:C1424–C1437 - PubMed
-
- Borges F, Fernandes E, Roleira F. (2002) Progress towards the discovery of xanthine oxidase inhibitors. Curr Med Chem 9:195–217 - PubMed
-
- Butler R, Morris AD, Belch JJ, Hill A, Struthers AD. (2000) Allopurinol normalizes endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetics with mild hypertension. Hypertension 35:746–751 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

