Telomeric protein TRF2 protects Holliday junctions with telomeric arms from displacement by the Werner syndrome helicase
- PMID: 20215438
- PMCID: PMC2896529
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq144
Telomeric protein TRF2 protects Holliday junctions with telomeric arms from displacement by the Werner syndrome helicase
Abstract
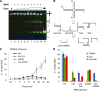
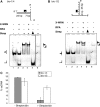
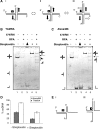
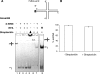
WRN protein loss causes Werner syndrome (WS), which is characterized by premature aging as well as genomic and telomeric instability. WRN prevents telomere loss, but the telomeric protein complex must regulate WRN activities to prevent aberrant telomere processing. Telomere-binding TRF2 protein inhibits telomere t-loop deletion by blocking Holliday junction (HJ) resolvase cleavage activity, but whether TRF2 also modulates HJ displacement at t-loops is unknown. In this study, we used multiplex fluorophore imaging to track the fate of individual strands of HJ substrates. We report the novel finding that TRF2 inhibits WRN helicase strand displacement of HJs with telomeric repeats in duplex arms, but unwinding of HJs with a telomeric center or lacking telomeric sequence is unaffected. These data, together with results using TRF2 fragments and TRF2 HJ binding assays, indicate that both the TRF2 B- and Myb domains are required to inhibit WRN HJ activity. We propose a novel model whereby simultaneous binding of the TRF2 B-domain to the HJ core and the Myb domain to telomeric arms promote and stabilize HJs in a stacked arm conformation that is unfavorable for unwinding. Our biochemical study provides a mechanistic basis for the cellular findings that TRF2 regulates WRN activity at telomeres.
Figures




References
-
- Kudlow BA, Kennedy BK, Monnat RJ., Jr Werner and Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndromes: mechanistic basis of human progeroid diseases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:394–404. - PubMed
-
- Opresko PL. Telomere ResQue and preservation–roles for the Werner syndrome protein and other RecQ helicases. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2008;129:79–90. - PubMed
-
- Chu WK, Hickson ID. RecQ helicases: multifunctional genome caretakers. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2009;9:644–654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

