An ErbB3 antibody, MM-121, is active in cancers with ligand-dependent activation
- PMID: 20215504
- PMCID: PMC2840205
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3145
An ErbB3 antibody, MM-121, is active in cancers with ligand-dependent activation
Abstract
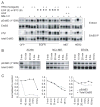
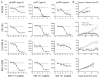
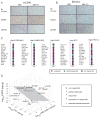
ErbB3 is a critical activator of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR; ErbB1), ErbB2 [human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)], and [hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET)] addicted cancers, and reactivation of ErbB3 is a prominent method for cancers to become resistant to ErbB inhibitors. In this study, we evaluated the in vivo efficacy of a therapeutic anti-ErbB3 antibody, MM-121. We found that MM-121 effectively blocked ligand-dependent activation of ErbB3 induced by either EGFR, HER2, or MET. Assessment of several cancer cell lines revealed that MM-121 reduced basal ErbB3 phosphorylation most effectively in cancers possessing ligand-dependent activation of ErbB3. In those cancers, MM-121 treatment led to decreased ErbB3 phosphorylation and, in some instances, decreased ErbB3 expression. The efficacy of single-agent MM-121 was also examined in xenograft models. A machine learning algorithm found that MM-121 was most effective against xenografts with evidence of ligand-dependent activation of ErbB3. We subsequently investigated whether MM-121 treatment could abrogate resistance to anti-EGFR therapies by preventing reactivation of ErbB3. We observed that an EGFR mutant lung cancer cell line (HCC827), made resistant to gefitinib by exogenous heregulin, was resensitized by MM-121. In addition, we found that a de novo lung cancer mouse model induced by EGFR T790M-L858R rapidly became resistant to cetuximab. Resistance was associated with an increase in heregulin expression and ErbB3 activation. However, concomitant cetuximab treatment with MM-121 blocked reactivation of ErbB3 and resulted in a sustained and durable response. Thus, these results suggest that targeting ErbB3 with MM-121 can be an effective therapeutic strategy for cancers with ligand-dependent activation of ErbB3.
Figures


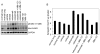
References
-
- Bianco R, Shin I, Ritter CA, et al. Loss of PTEN/MMAC1/TEP in EGF receptor-expressing tumor cells counteracts the antitumor action of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncogene. 2003;22:2812–22. - PubMed
-
- Moulder SL, Yakes FM, Muthuswamy SK, Bianco R, Simpson JF, Arteaga CL. Epidermal growth factor receptor (HER1) tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 (Iressa) inhibits HER2/neu (erbB2)-overexpressing breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2001;61:8887–95. - PubMed
-
- Yakes FM, Chinratanalab W, Ritter CA, King W, Seelig S, Arteaga CL. Herceptin-induced inhibition of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and Akt Is required for antibody-mediated effects on p27, cyclin D1, and antitumor action. Cancer Res. 2002;62:4132–41. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 2007;316:1039–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K08 AG024004/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA137008/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA120060/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA137008/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG2400401/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA120060/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027757/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA127003/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140594/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA090578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA127003/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA140594/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

