Transcriptional pathway signatures predict MEK addiction and response to selumetinib (AZD6244)
- PMID: 20215513
- PMCID: PMC3166660
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1577
Transcriptional pathway signatures predict MEK addiction and response to selumetinib (AZD6244)
Abstract
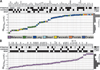
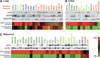
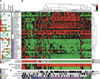
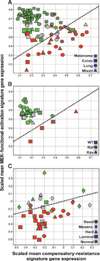
Selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886) is a selective, non-ATP-competitive inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase (MEK)-1/2. The range of antitumor activity seen preclinically and in patients highlights the importance of identifying determinants of response to this drug. In large tumor cell panels of diverse lineage, we show that MEK inhibitor response does not have an absolute correlation with mutational or phospho-protein markers of BRAF/MEK, RAS, or phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) activity. We aimed to enhance predictivity by measuring pathway output through coregulated gene networks displaying differential mRNA expression exclusive to resistant cell subsets and correlated to mutational or dynamic pathway activity. We discovered an 18-gene signature enabling measurement of MEK functional output independent of tumor genotype. Where the MEK pathway is activated but the cells remain resistant to selumetinib, we identified a 13-gene signature that implicates the existence of compensatory signaling from RAS effectors other than PI3K. The ability of these signatures to stratify samples according to functional activation of MEK and/or selumetinib sensitivity was shown in multiple independent melanoma, colon, breast, and lung tumor cell lines and in xenograft models. Furthermore, we were able to measure these signatures in fixed archival melanoma tumor samples using a single RT-qPCR-based test and found intergene correlations and associations with genetic markers of pathway activity to be preserved. These signatures offer useful tools for the study of MEK biology and clinical application of MEK inhibitors, and the novel approaches taken may benefit other targeted therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Basal and treatment-induced activation of AKT mediates resistance to cell death by AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in Braf-mutant human cutaneous melanoma cells.Cancer Res. 2010 Nov 1;70(21):8736-47. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0902. Epub 2010 Oct 19. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20959481 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of common predictive markers of in vitro response to the Mek inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244; ARRY-142886) in human breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Jul;9(7):1985-94. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0037. Epub 2010 Jun 29. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20587667 Free PMC article.
-
Horizontal Combination of MEK and PI3K/mTOR Inhibition in BRAF Mutant Tumor Cells with or without Concomitant PI3K Pathway Mutations.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 16;21(20):7649. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207649. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33081092 Free PMC article.
-
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR cascade inhibitors: how mutations can result in therapy resistance and how to overcome resistance.Oncotarget. 2012 Oct;3(10):1068-111. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.659. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 23085539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutations and deregulation of Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR cascades which alter therapy response.Oncotarget. 2012 Sep;3(9):954-87. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.652. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 23006971 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RAF265 inhibits the growth of advanced human melanoma tumors.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Apr 15;18(8):2184-98. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1122. Epub 2012 Feb 20. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22351689 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of pan-RAF and MEK inhibitors in NRAS mutant melanoma.Mol Cancer. 2015 Feb 3;14(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0293-5. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25645078 Free PMC article.
-
An integrative gene expression signature analysis identifies CMS4 KRAS-mutated colorectal cancers sensitive to combined MEK and SRC targeted therapy.BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 10;22(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09344-3. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35272617 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Determinants of Response to Pembrolizumab Monotherapy across Solid Tumor Types.Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Apr 14;28(8):1680-1689. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-3329. Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 34965943 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Signature-Based Approach Identified MEK1/2 as a Potential Target Associated With Relapse After Anti-TNFα Treatment for Crohn's Disease.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2018 May 18;24(6):1251-1265. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izy079. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2018. PMID: 29669006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davies BR, Logie A, McKay JS, et al. AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), a potent inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1/2 kinases: mechanism of action in vivo, pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship, and potential for combination in preclinical models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:2209–2219. - PubMed
-
- Brose MS, Volpe P, Feldman M, et al. BRAF and RAS mutations in human lung cancer and melanoma. Cancer Res. 2002;62:6997–7000. - PubMed
-
- Sebolt-Leopold JS, Dudley DT, Herrera R, et al. Blockade of the MAP kinase pathway suppresses growth of colon tumors in vivo. Nat Med. 1999;5:810–816. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

