Targeting multiple kinase pathways: a change in paradigm
- PMID: 20215532
- PMCID: PMC2875112
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-3182
Targeting multiple kinase pathways: a change in paradigm
Abstract
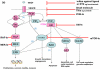
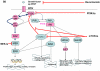
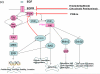
Anticancer drugs that target protein kinases include small molecule inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies. Feedback loops and cross talk between signaling pathways impact significantly on the efficacy of cancer therapeutics, and resistance to targeted agents is a major barrier to effective treatments. Increasingly, therapies are being designed to target multiple kinase pathways. This can be achieved using a single agent that inhibits multiple signaling pathways or a combination of highly selective agents. In this review we discuss the principles of specifically targeting multiple kinase pathways with particular reference to angiogenic signaling pathways.
Copyright 2010 AACR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New paradigms in anticancer therapy: targeting multiple signaling pathways with kinase inhibitors.Semin Oncol. 2006 Aug;33(4):407-20. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2006.04.005. Semin Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16890796 Review.
-
Therapeutic protein kinase inhibitors.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Apr;66(7):1163-77. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8539-7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19011754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein kinases as targets for cancer treatment.Pharmacogenomics. 2007 Aug;8(8):1005-16. doi: 10.2217/14622416.8.8.1005. Pharmacogenomics. 2007. PMID: 17716234 Review.
-
Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors.Nat Rev Cancer. 2009 Jan;9(1):28-39. doi: 10.1038/nrc2559. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19104514 Review.
-
Challenges of developing therapeutics that target signal transduction in patients with gynecologic and other malignancies.J Clin Oncol. 2003 May 15;21(10 Suppl):175s-186s. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.01.146. J Clin Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12743132 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of histidine kinase inhibitors and their biological properties.Med Res Rev. 2020 Jul;40(4):1440-1495. doi: 10.1002/med.21651. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Med Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 31802520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tetraspecific ligand for tumor-targeted delivery of nanomaterials.Biomaterials. 2014 Jul;35(23):6026-36. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.04.015. Epub 2014 Apr 28. Biomaterials. 2014. PMID: 24786763 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated disease progression after discontinuation of sorafenib in a patient with metastatic papillary thyroid cancer.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2014 Sep;29(3):388-93. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2014.29.3.388. Epub 2014 Sep 25. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2014. PMID: 25309799 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Histidine Kinase and the Development of Its Inhibitors in the 21st Century.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jun 22;13(7):576. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070576. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dynamic nature of the kinome.Biochem J. 2013 Feb 15;450(1):1-8. doi: 10.1042/BJ20121456. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23343193 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kantarjian H, Sawyers C, Hochhaus A, Guilhot F, Schiffer C, Gambacorti-Passerini C, et al. Hematologic and cytogenetic responses to imatinib mesylate in chronic myelogenous leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2002 Feb 28;346(9):645–52. - PubMed
-
- Dudek AZ, Zolnierek J, Dham A, Lindgren BR, Szczylik C. Sequential therapy with sorafenib and sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2009 Jan 1;115(1):61–7. - PubMed
-
- Sablin MP, Negrier S, Ravaud A, Oudard S, Balleyguier C, Gautier J, et al. Sequential sorafenib and sunitinib for renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2009 Jul;182(1):29–34. discussion. - PubMed
-
- Fox SB, Gasparini G, Harris AL. Angiogenesis: pathological, prognostic, and growth-factor pathways and their link to trial design and anticancer drugs. Lancet Oncol. 2001 May;2(5):278–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

