The Arabidopsis thaliana Myo-inositol 1-phosphate synthase1 gene is required for Myo-inositol synthesis and suppression of cell death
- PMID: 20215587
- PMCID: PMC2861443
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.109.071779
The Arabidopsis thaliana Myo-inositol 1-phosphate synthase1 gene is required for Myo-inositol synthesis and suppression of cell death
Abstract
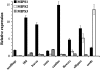
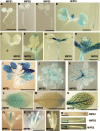
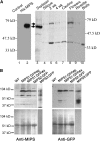
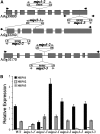
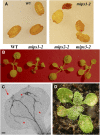
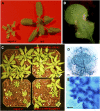
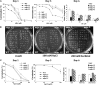
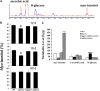
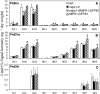
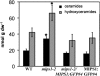
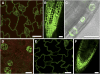
l-myo-inositol 1-phosphate synthase (MIPS; EC 5.5.1.4) catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the synthesis of myo-inositol, a critical compound in the cell. Plants contain multiple MIPS genes, which encode highly similar enzymes. We characterized the expression patterns of the three MIPS genes in Arabidopsis thaliana and found that MIPS1 is expressed in most cell types and developmental stages, while MIPS2 and MIPS3 are mainly restricted to vascular or related tissues. MIPS1, but not MIPS2 or MIPS3, is required for seed development, for physiological responses to salt and abscisic acid, and to suppress cell death. Specifically, a loss in MIPS1 resulted in smaller plants with curly leaves and spontaneous production of lesions. The mips1 mutants have lower myo-inositol, ascorbic acid, and phosphatidylinositol levels, while basal levels of inositol (1,4,5)P(3) are not altered in mips1 mutants. Furthermore, mips1 mutants exhibited elevated levels of ceramides, sphingolipid precursors associated with cell death, and were complemented by a MIPS1-green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion construct. MIPS1-, MIPS2-, and MIPS3-GFP each localized to the cytoplasm. Thus, MIPS1 has a significant impact on myo-inositol levels that is critical for maintaining levels of ascorbic acid, phosphatidylinositol, and ceramides that regulate growth, development, and cell death.
Figures
Comment in
-
Myo-inositol biosynthesis genes in Arabidopsis: differential patterns of gene expression and role in cell death.Plant Cell. 2010 Mar;22(3):537. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.220310. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Plant Cell. 2010. PMID: 20233949 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alcazar-Roman A.R., Tran E.J., Guo S., Wente S.R. (2006). Inositol hexakisphosphate and Gle1 activate the DEAD-box protein Dbp5 for nuclear mRNA export. Nat. Cell Biol. 8: 711–716 - PubMed
-
- Alcazar-Roman A.R., Wente S.R. (2008). Inositol polyphosphates: A new frontier for regulating gene expression. Chromosoma 117: 1–13 - PubMed
-
- Allison J.H., Stewart M.A. (1973). Myo-inositol and ascorbic acid in developing rat brain. J. Neurochem. 20: 1785–1788 - PubMed
-
- Alonso J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

