Neonatal pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 20216169
- PMCID: PMC2843001
- DOI: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e3181c76cdc
Neonatal pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
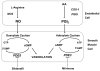
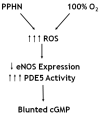
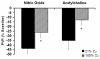
When the normal cardiopulmonary transition fails to occur, the result is persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Severe persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn is estimated to occur in 2 per 1000 live-born term infants, and some degree of pulmonary hypertension complicates the course of >10% of all neonates with respiratory failure. This review article discusses the vascular abnormalities that are associated with neonatal pulmonary hypertension, including recognition of its role in severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants. A systematic review of the evidence for common therapies including inhaled nitric oxide, high-frequency ventilation, surfactant, and extracorporeal life support is included. Finally, this field is rapidly evolving, and the rationale for promising new treatment approaches is reviewed, including inhibition of phosphodiesterases and scavengers of reactive oxygen species.
Figures
References
-
- Abman SH, Chatfield BA, Hall SL, McMurtry IF. Role of endothelium-derived relaxing factor during transition of pulmonary circulation at birth. Am J Physiol. 1990;259:H1921–H1927. - PubMed
-
- Pierce CM, Krywawych S, Petros AJ. Asymmetric dimethyl arginine and symmetric dimethyl arginine levels in infants with persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2004;5:517–520. - PubMed
-
- Pearson DL, Dawling S, Walsh WF, Haines JL, Christman BW, Bazyk A, Scott N, Summar ML. Neonatal pulmonary hypertension--urea-cycle intermediates, nitric oxide production, and carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase function. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1832–1838. - PubMed
-
- Brannon TS, MacRitchie AN, Jaramillo MA, Sherman TS, Yuhanna IS, Margraf LR, Shaul PW. Ontogeny of cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression in ovine lung. Am J Physiol. 1998;274:L66–L71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

