Gantacurium and CW002 do not potentiate muscarinic receptor-mediated airway smooth muscle constriction in guinea pigs
- PMID: 20216393
- PMCID: PMC2854830
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181d32016
Gantacurium and CW002 do not potentiate muscarinic receptor-mediated airway smooth muscle constriction in guinea pigs
Abstract
Background: Neuromuscular blocking agents are an integral component of general anesthesia. In addition to their intended pharmacologic target on skeletal muscle nicotinic receptors, undesirable airway effects (i.e., bronchoconstriction) can result from neuromuscular blocking agents' affinity for airway muscarinic receptors. We questioned whether two new members of a bisquaternary nondepolarizing muscle relaxant family, gantacurium and CW002, demonstrated detrimental effects of airway muscarinic receptors using an in vivo model in guinea pig airways.
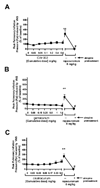
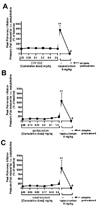
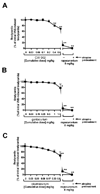
Methods: Urethane-anesthetized male guinea pigs were ventilated through a tracheostomy with continuous digital recordings of pulmonary inflation pressure and heart rate. The dose for 95% twitch suppression for gantacurium, CW002, cisatracurium, and rapacuronium was defined in the guinea pig. Transient and reproducible changes in pulmonary inflation pressure and heart rate were recorded after vagal nerve stimulation or intravenous injection of acetylcholine before and after pretreatment with cumulatively increasing concentrations of gantacurium, CW002, cisatracurium or a single concentration of rapacuronium.
Results: The doses for 95% twitch suppression for gantacurium, CW002, cisatracurium, and rapacuronium were 0.064 +/- 0.006, 0.012 +/- 0.0006, 0.10 +/- 0.003, and 0.31 +/- 0.05 mg/kg, respectively. Gantacurium, CW002, and cisatracurium were without effects on baseline pulmonary inflation pressures and were devoid of significant interactions with M2 and M3 muscarinic receptors in vivo.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that gantacurium and CW002 are devoid of significant effects at airway muscarinic receptors particularly M3 receptors on bronchial smooth musculature at doses several fold higher than those required for functional muscle paralysis.
Similar articles
-
Neuromuscular blocking agents' differential bronchoconstrictive potential in Guinea pig airways.Anesthesiology. 2007 Apr;106(4):763-72. doi: 10.1097/01.anes.0000264763.48920.c9. Anesthesiology. 2007. PMID: 17413914
-
Rapacuronium preferentially antagonizes the function of M2 versus M3 muscarinic receptors in guinea pig airway smooth muscle.Anesthesiology. 2005 Jan;102(1):117-24. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200501000-00020. Anesthesiology. 2005. PMID: 15618795
-
A mechanism for rapacuronium-induced bronchospasm: M2 muscarinic receptor antagonism.Anesthesiology. 2003 Apr;98(4):906-11. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200304000-00017. Anesthesiology. 2003. PMID: 12657852
-
Newer neuromuscular blocking agents: how do they compare with established agents?Drugs. 2001;61(7):919-42. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200161070-00003. Drugs. 2001. PMID: 11434449 Review.
-
Muscarinic receptors and control of airway smooth muscle.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998 Nov;158(5 Pt 3):S154-60. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.158.supplement_2.13tac120. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. PMID: 9817739 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural Modification in Anesthetic Drug Development for Prodrugs and Soft Drugs.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 1;13:923353. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.923353. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35847008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep Neuromuscular Block Attenuates Chronic Postsurgical Pain and Enhances Long-Term Postoperative Recovery After Spinal Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Pain Ther. 2023 Aug;12(4):1055-1064. doi: 10.1007/s40122-023-00528-8. Epub 2023 Jun 6. Pain Ther. 2023. PMID: 37278923 Free PMC article.
-
New Drug Developments for Neuromuscular Blockade and Reversal: Gantacurium, CW002, CW011, and Calabadion.Curr Anesthesiol Rep. 2018;8(2):119-124. doi: 10.1007/s40140-018-0262-9. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Curr Anesthesiol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29904284 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moss J, Rosow CE. Histamine release by narcotics and muscle relaxants in humans. Anesthesiology. 1983;59:330–339. - PubMed
-
- North FC, Kettelkamp N, Hirshman CA. Comparison of cutaneous and in vitro histamine release by muscle relaxants. Anesthesiology. 1987;66:543–546. - PubMed
-
- Okanlami OA, Fryer AD, Hirshman CA. Interaction of nondepolarizing muscle relaxants with m2 and m3 muscarinic receptors in guinea pig lung and heart. Anesthesiology. 1996;84:155–161. - PubMed
-
- Jooste EH, Sharma A, Zhang Y, Emala CW. Rapacuronium augments acetylcholine-induced bronchoconstriction via positive allosteric interactions at the M3 muscarinic receptor. Anesthesiology. 2005;103:1195–1203. - PubMed
-
- Jooste E, Zhang Y, Emala CW. Neuromuscular blocking agents' differential bronchoconstrictive potential in Guinea pig airways. Anesthesiology. 2007;106:763–772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources