Pulmonary cystic echinococcosis
- PMID: 20216420
- PMCID: PMC3362862
- DOI: 10.1097/MCP.0b013e3283386282
Pulmonary cystic echinococcosis
Abstract
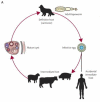
Purpose of review: Pulmonary cystic echinococcosis, a zoonosis caused by the larvae of the dog tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus, is considered as a major public health problem in countries where dogs are used to care for large herds. Despite its frequency and widespread endemicity, the literature on pulmonary cystic echinococcosis is scarce and not systematic. We aimed to summarize currently available information to provide a comprehensive overview for clinicians facing cases of pulmonary cystic echinococcosis.
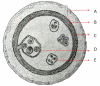
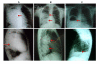
Recent findings: Despite discrepancies in the literature, some patterns can be discerned. The ratio of lung:liver involvement is higher in children than in adults. Most pulmonary cases are discovered incidentally on routine radiograph evaluation; also most infected individuals remain asymptomatic until the cyst enlarges sufficiently to cause symptoms. Symptoms are usually caused by mass effect from the cyst. Complications (cyst rupture, aggregated infection) change the clinical presentation, producing cough, chest pain, hemoptysis, or vomica. Diagnosis is obtained by chest radiographs or computed tomography, and supported by serology. Presurgical chemotherapy reduces the chances of seeding and recurrence. Treatment with benzimidazoles is an option when surgery is unavailable or complete removal is unfeasible.
Summary: Diagnosis of pulmonary cystic echinococcosis is primarily made by imaging, and surgery remains the main therapeutic approach.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Surgical Therapy of Pulmonal Echinococcosis].Zentralbl Chir. 2019 Sep;144(S 01):S46-S56. doi: 10.1055/a-0851-4199. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Zentralbl Chir. 2019. PMID: 31484205 German.
-
8-year old patient with giant hydatid cyst consulted with chest wall asymmetry.Pediatr Int. 2015 Dec;57(6):1164-6. doi: 10.1111/ped.12811. Pediatr Int. 2015. PMID: 26711916
-
[Clinical problems in medical mycology: problem no. 14. Pulmonary hydatid cyst].Rev Iberoam Micol. 2004 Dec;21(4):216-7. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2004. PMID: 15709806 Spanish. No abstract available.
-
Management of echinococcosis.J Assoc Physicians India. 2006 Jun;54:458-62. J Assoc Physicians India. 2006. PMID: 16909694 Review.
-
[Cystic echinococcosis in humans: our clinic experience].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):45-51. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305685 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Anaphylaxis due to ruptured pulmonary hydatid cyst in a 13-year-old boy.Asia Pac Allergy. 2015 Apr;5(2):128-31. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2015.5.2.128. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Asia Pac Allergy. 2015. PMID: 25938078 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary cystic echinococcosis acquired during a short-term tourist travel.IDCases. 2023 Jun 28;33:e01833. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2023.e01833. eCollection 2023. IDCases. 2023. PMID: 37448378 Free PMC article.
-
Isolated pulmonary hydatid cyst: Misinterpreted as metastatic pulmonary lesion in an operated case of carcinoma breast in young female.J Family Med Prim Care. 2016 Jul-Sep;5(3):701-703. doi: 10.4103/2249-4863.197299. J Family Med Prim Care. 2016. PMID: 28217612 Free PMC article.
-
Cured Transudative Pleural Effusion: A Case Report.Tanaffos. 2016;15(2):121-123. Tanaffos. 2016. PMID: 27904546 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of hospital records of children with hydatid cyst in south of Iran.J Parasit Dis. 2017 Dec;41(4):1044-1048. doi: 10.1007/s12639-017-0932-4. Epub 2017 Jun 24. J Parasit Dis. 2017. PMID: 29114140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moro P, Schantz PM. Echinococcosis: a review. Int J Infect Dis. 2009;13:125–133. - PubMed
-
- Garcia HH, Moro PL, Schantz PM. Zoonotic helminth infections of humans: echinococcosis, cysticercosis and fascioliasis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2007;20:489–494. - PubMed
-
- Craig PS, McManus DP, Lightowlers MW, et al. Prevention and control of cystic echinococcosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7:385–394. - PubMed
-
- Arroud M, Afifi MA, El Ghazi K, et al. Lung hydatic cysts in children: comparison study between giant and non-giant cysts. Pediatr Surg Int. 2009;25:37–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

