Targeted delivery of siRNA to macrophages for anti-inflammatory treatment
- PMID: 20216529
- PMCID: PMC2890121
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2010.27
Targeted delivery of siRNA to macrophages for anti-inflammatory treatment
Abstract
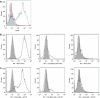
Inflammation mediated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and the associated neuronal apoptosis characterizes a number of neurologic disorders. Macrophages and microglial cells are believed to be the major source of TNF-alpha in the central nervous system (CNS). Here, we show that suppression of TNF-alpha by targeted delivery of small interfering RNA (siRNA) to macrophage/microglial cells dramatically reduces lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis in vivo. Because macrophage/microglia express the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AchR) on their surface, we used a short AchR-binding peptide derived from the rabies virus glycoprotein (RVG) as a targeting ligand. This peptide was fused to nona-D-arginine residues (RVG-9dR) to enable siRNA binding. RVG-9dR was able to deliver siRNA to induce gene silencing in macrophages and microglia cells from wild type, but not AchR-deficient mice, confirming targeting specificity. Treatment with anti-TNF-alpha siRNA complexed to RVG-9dR achieved efficient silencing of LPS-induced TNF-alpha production by primary macrophages and microglia cells in vitro. Moreover, intravenous injection with RVG-9dR-complexed siRNA in mice reduced the LPS-induced TNF-alpha levels in blood as well as in the brain, leading to a significant reduction in neuronal apoptosis. These results demonstrate that RVG-9dR provides a tool for siRNA delivery to macrophages and microglia and that suppression of TNF-alpha can potentially be used to suppress neuroinflammation in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Silencing TNF-α in macrophages and dendritic cells for arthritis treatment.Scand J Rheumatol. 2013;42(4):266-9. doi: 10.3109/03009742.2013.777779. Epub 2013 Apr 14. Scand J Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23582054
-
Transvascular delivery of small interfering RNA to the central nervous system.Nature. 2007 Jul 5;448(7149):39-43. doi: 10.1038/nature05901. Epub 2007 Jun 17. Nature. 2007. PMID: 17572664
-
Targeted delivery of small interfering RNA to human dendritic cells to suppress dengue virus infection and associated proinflammatory cytokine production.J Virol. 2010 Mar;84(5):2490-501. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02105-08. Epub 2009 Dec 16. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20015996 Free PMC article.
-
The potential use of rabies virus glycoprotein-derived peptides to facilitate drug delivery into the central nervous system: a mini review.J Drug Target. 2017 Jun;25(5):379-385. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2016.1223676. Epub 2016 Aug 31. J Drug Target. 2017. PMID: 27581650 Review.
-
Reverse Signaling of Tumor Necrosis Factor Superfamily Proteins in Macrophages and Microglia: Superfamily Portrait in the Neuroimmune Interface.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 19;10:262. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00262. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30838001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Supramolecular self-assembled nanoparticles mediate oral delivery of therapeutic TNF-α siRNA against systemic inflammation.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013 May 27;52(22):5757-61. doi: 10.1002/anie.201209991. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013. PMID: 23610013 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Systemic RNAi-mediated Gene Silencing in Nonhuman Primate and Rodent Myeloid Cells.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2012 Jan 24;1(1):e4. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2011.3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2012. PMID: 23344621 Free PMC article.
-
MUTYH promotes oxidative microglial activation and inherited retinal degeneration.JCI Insight. 2016 Sep 22;1(15):e87781. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.87781. JCI Insight. 2016. PMID: 27699246 Free PMC article.
-
Increased brain radioactivity by intranasal P-labeled siRNA dendriplexes within in situ-forming mucoadhesive gels.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:1373-85. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S28261. Epub 2012 Mar 12. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22457595 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Nipah virus immune-antagonism strategy revealed by experimental and computational study.J Virol. 2010 Nov;84(21):10965-73. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01335-10. Epub 2010 Aug 25. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20739535 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu J, Liu Y, Zhang H, Chen G, Wang K., and , Xiao X. KLF4 promotes the expression, translocation, and releas eof HMGB1 in RAW264.7 macrophages in response to LPS. Shock. 2008;30:260–266. - PubMed
-
- Czapski GA, Cakala M, Chalimoniuk M, Gajkowska B., and , Strosznajder JB. Role of nitric oxide in the brain during lipopolysaccharide-evoked systemic inflammation. J Neurosci Res. 2007;85:1694–1703. - PubMed
-
- Perry VH, Newman TA., and , Cunningham C. The impact of systemic infection on the progression of neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4:103–112. - PubMed
-
- Emerit J, Edeas M., and , Bricaire F. Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother. 2004;58:39–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

