Nucleoprotein Diet Ameliorates Arthritis Symptoms in Mice Transgenic for Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type I (HTLV-1)
- PMID: 20216941
- PMCID: PMC2831098
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.09-61
Nucleoprotein Diet Ameliorates Arthritis Symptoms in Mice Transgenic for Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type I (HTLV-1)
Abstract
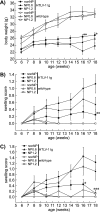
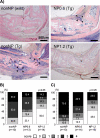
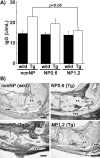
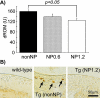
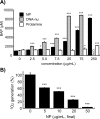
Because rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an autoimmune disease, the patients often recognize side-effects due to the medication, alternative therapeutic strategies might potentially offer a clinical advantage. We evaluated the effect of nucleoprotein from salmon soft roe on animal model of arthritis. Mice transgenic for human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-1 Tg) were divided into three experimental groups and supplemented on either nucleoprotein-free (nonNP), or 0.6% or 1.2% nucleoprotein mixed (NP0.6 or NP1.2) diet for 3 months. The mice were evaluated arthritis by morphology, and measured with rheumatoid factor (RF). Moreover, macrophages and oxidative metabolites were assessed in the ankle and/or serum. Anti-oxidative potentials in nucleoprotein were determined with biological anti-oxidative potential (BAP) test, and electron spin resonance (ESR) analysis. NonNP-diet HTLV-1 Tg mice increased an arthritis symptoms and RF. The symptoms were ameliorated in NP-diet groups. Macrophages detected by F4/80 staining, and oxidative metabolites in the serum and/or joints were clearly decreased in 1.2% NP-diet HTLV-1 Tg mice. Nucleoprotein and DNA-nucleotide, but less protamine, had direct anti-oxidative potency with BAP test and/or ESR in vitro. These observations suggest that dietary nucleoprotein ameliorates arthritis symptoms in HTLV-1 Tg mice and offers hope as an alternative treatment for this debilitating medical condition.
Keywords: alternative medicine; nucleoprotein; radical scavenger; rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures


References
-
- Firestein G.S., Zvaifler N.J. . In: Rheumatoid arthritis: a disease of disordered immunity. in Inflammation: basic principles and clinical correlates. Gallin J.I., Goldstein I.M., Synderman R., editors. New York: Raven Press; 1992. pp. 959–75.
-
- Vaughan J.H. 1992 Joseph J. Bunim Lecture: Pathogenetic concepts and origins of rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993;36:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Andriopoulos N.A., Mestecky J., Miller E.J., Bradley E.L. Antibodies to native and denatured collagens in sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1976;19:613–617. - PubMed
-
- van Eden W., Thole J.E., van der Zee R., Noordzij A., van Embden J.D., Hensen E.J., Cohen I.R. Cloning of the mycobacterial epitope recognized by T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. Nature. 1988;331:171–173. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

