Effectiveness of hydrogen rich water on antioxidant status of subjects with potential metabolic syndrome-an open label pilot study
- PMID: 20216947
- PMCID: PMC2831093
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.09-100
Effectiveness of hydrogen rich water on antioxidant status of subjects with potential metabolic syndrome-an open label pilot study
Abstract
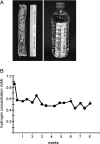
Metabolic syndrome is characterized by cardiometabolic risk factors that include obesity, insulin resistance, hypertension and dyslipidemia. Oxidative stress is known to play a major role in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome. The objective of this study was to examine the effectiveness of hydrogen rich water (1.5-2 L/day) in an open label, 8-week study on 20 subjects with potential metabolic syndrome. Hydrogen rich water was produced, by placing a metallic magnesium stick into drinking water (hydrogen concentration; 0.55-0.65 mM), by the following chemical reaction; Mg + 2H(2)O --> Mg (OH)(2) + H(2). The consumption of hydrogen rich water for 8 weeks resulted in a 39% increase (p<0.05) in antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD) and a 43% decrease (p<0.05) in thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) in urine. Further, subjects demonstrated an 8% increase in high density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterol and a 13% decrease in total cholesterol/HDL-cholesterol from baseline to week 4. There was no change in fasting glucose levels during the 8 week study. In conclusion, drinking hydrogen rich water represents a potentially novel therapeutic and preventive strategy for metabolic syndrome. The portable magnesium stick was a safe, easy and effective method of delivering hydrogen rich water for daily consumption by participants in the study.
Keywords: drinking water; hydrogen; magnesium; metabolic syndrome; oxidative stress.
Figures
References
-
- Ford E.S., Giles W.H., Dietz W.H. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US adults: findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA. 2002;287:356–359. - PubMed
-
- Grundy S.M., Brewer H.B. Jr., Cleeman J.I., Smith S.C.Jr., Lenfant C. Definition of metabolic syndrome: Report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/American Heart Association conference on scientific issues related to definition. Circulation. 2004;109:433–438. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

