Regional spread of HIV-1 M subtype B in middle-aged patients by random env-C2V4 region sequencing
- PMID: 20217125
- PMCID: PMC2854364
- DOI: 10.1007/s00430-010-0145-2
Regional spread of HIV-1 M subtype B in middle-aged patients by random env-C2V4 region sequencing
Abstract
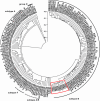
A transmission cluster of HIV-1 M:B was identified in 11 patients with a median age of 52 (range 26-65) in North-East Germany by C2V4 region sequencing of the env gene of HIV-1, who-except of one-were not aware of any risky behaviour. The 10 male and 1 female patients deteriorated immunologically, according to their information made available, within 4 years after a putative HIV acquisition. Nucleic acid sequence analysis showed a R5 virus in all patients and in 7 of 11 a crown motif of the V3 loop, GPGSALFTT, which is found rarely. Analysis of formation of this cluster showed that there is still a huge discrepancy between awareness and behaviour regarding HIV transmission in middle-aged patients, and that a local outbreak can be detected by nucleic acid analysis of the hypervariable env region.
Figures
References
-
- Gottlieb MD, Schroff R, Schanker HM, Weissman JD, Fan PT, Wolf RA, Saxon A. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and mucosal candidiasis in previously healthy homosexual men. N Engl J Med. 1981;305:1425–1431. - PubMed
-
- Hamouda O, Marcus U, Voss I, Kollan C. Epidemiology of HIV infection in Germany. Bundesgesundbl Gesundforsch Gesundschutz. 2007;50:399–411. - PubMed
-
- Van de Peer Y, De Wachter R. Construction of evolutionary distance trees with Treecon for Windows: accounting for variation in nucleotide substitution rate among sites. Comput Appl Biosci. 1997;13:227–230. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

