Recombinant Moraxella bovoculi cytotoxin-ISCOM matrix adjuvanted vaccine to prevent naturally occurring infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis
- PMID: 20217228
- PMCID: PMC2855018
- DOI: 10.1007/s11259-010-9347-8
Recombinant Moraxella bovoculi cytotoxin-ISCOM matrix adjuvanted vaccine to prevent naturally occurring infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis
Abstract
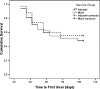
A randomized, blinded, controlled field trial was conducted during summer 2006 in a northern California, USA, herd of beef cattle to evaluate the efficacy of a recombinant Moraxella bovoculi cytotoxin subunit vaccine to prevent naturally occurring infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis (IBK; pinkeye). A convenience sample comprised of 127 steers were administered a subcutaneous dose of either adjuvant alone (ISCOM matrices; control group) or recombinant M. bovoculi cytotoxin carboxy terminus adjuvanted with ISCOM matrices (MbvA group) and were boostered 21 days later. The steers were examined once weekly for 15 weeks for evidence of IBK. No significant difference in the cumulative proportion of corneal ulcerations was detected between groups. Compared to the control calves, the MbvA vaccinates had significantly higher increases in serum neutralizing titers to M. bovoculi hemolysin between week 0 and week 6. The prevalence of M. bovis isolations was higher from ulcerated eyes of calves vaccinated with MbvA as compared to control calves. Vaccination of calves against the carboxy terminus of M. bovoculi RTX toxin resulted in significant increases in serum hemolysin neutralizing titers and may modulate organism type cultured from ulcerated eyes of calves in herds where both M. bovis and M. bovoculi exist. Use of M. bovoculi antigens alone in vaccines to prevent IBK may not be beneficial in herds where IBK is associated with both M. bovoculi and M. bovis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevention of naturally occurring infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis with a recombinant Moraxella bovis pilin-Moraxella bovis cytotoxin-ISCOM matrix adjuvanted vaccine.Vet Microbiol. 2007 Dec 15;125(3-4):274-83. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2007.05.028. Epub 2007 Jun 14. Vet Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17656049 Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized controlled field trial to assess efficacy of a Moraxella bovis pilin-cytotoxin-Moraxella bovoculi cytotoxin subunit vaccine to prevent naturally occurring infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis.Am J Vet Res. 2012 Oct;73(10):1670-5. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.73.10.1670. Am J Vet Res. 2012. PMID: 23013196 Clinical Trial.
-
Prevention of naturally occurring infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis with a recombinant Moraxella bovis cytotoxin-ISCOM matrix adjuvanted vaccine.Vaccine. 2004 Dec 9;23(4):537-45. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.06.025. Vaccine. 2004. PMID: 15530703 Clinical Trial.
-
Bovine Immune Responses to Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi Following Vaccination and Natural or Experimental Infections.Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2021 Jul;37(2):253-266. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2021.03.002. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2021. PMID: 34049657 Review.
-
Component Causes of Infectious Bovine Keratoconjunctivitis - The Role of Moraxella Species in the Epidemiology of Infectious Bovine Keratoconjunctivitis.Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2021 Jul;37(2):279-293. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2021.03.004. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2021. PMID: 34049659 Review.
Cited by
-
Large genomic differences between Moraxella bovoculi isolates acquired from the eyes of cattle with infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis versus the deep nasopharynx of asymptomatic cattle.Vet Res. 2016 Feb 13;47:31. doi: 10.1186/s13567-016-0316-2. Vet Res. 2016. PMID: 26872821 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic differences among Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi isolates from infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis (IBK) outbreaks in southern Brazil.Genet Mol Biol. 2020 May 29;43(2):e20180380. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2018-0380. eCollection 2020. Genet Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32478794 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of eye patches on corneal ulcer healing and weight gain in stocker steers on pasture: a randomized controlled trial.Transl Anim Sci. 2021 Sep 23;5(4):txab162. doi: 10.1093/tas/txab162. eCollection 2021 Oct. Transl Anim Sci. 2021. PMID: 34693213 Free PMC article.
-
Bovine ocular microbiome: the next frontier in managing Pinkeye in cattle.Anim Microbiome. 2025 Jun 4;7(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s42523-025-00425-9. Anim Microbiome. 2025. PMID: 40468436 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence factors of Moraxella catarrhalis outer membrane vesicles are major targets for cross-reactive antibodies and have adapted during evolution.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 21;8(1):4955. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23029-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29563531 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources