Anterior ankle arthroscopy, distraction or dorsiflexion?
- PMID: 20217392
- PMCID: PMC2855029
- DOI: 10.1007/s00167-010-1089-1
Anterior ankle arthroscopy, distraction or dorsiflexion?
Abstract
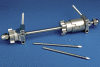
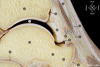
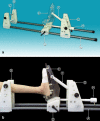
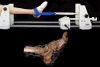
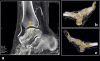
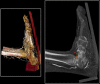
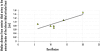
Anterior ankle arthroscopy can basically be performed by two different methods; the dorsiflexion- or distraction method. The objective of this study was to determine the size of the anterior working area for both the dorsiflexion and distraction method. The anterior working area is anteriorly limited by the overlying anatomy which includes the neurovascular bundle. We hypothesize that in ankle dorsiflexion the anterior neurovascular bundle will move away anteriorly from the ankle joint, whereas in ankle distraction the anterior neurovascular bundle is pulled tight towards the joint, thereby decreasing the safe anterior working area. Six fresh frozen ankle specimens, amputated above the knee, were scanned with computed tomography. Prior to scanning the anterior tibial artery was injected with contrast fluid and subsequently each ankle was scanned both in ankle dorsiflexion and in distraction. A special device was developed to reproducibly obtain ankle dorsiflexion and distraction in the computed tomography scanner. The distance between the anterior border of the inferior tibial articular facet and the posterior border of the anterior tibial artery was measured. The median distance from the anterior border of the inferior tibial articular facet to the posterior border of the anterior tibial artery in ankle dorsiflexion and distraction was 0.9 cm (range 0.7-1.5) and 0.7 cm (range 0.5-0.8), respectively. The distance in ankle dorsiflexion significantly exceeded the distance in ankle distraction (P = 0.03). The current study shows a significantly increased distance between the anterior distal tibia and the overlying anterior neurovascular bundle with the ankle in a slightly dorsiflexed position as compared to the distracted ankle position. We thereby conclude that the distracted ankle position puts the neurovascular structures more at risk for iatrogenic damage when performing anterior ankle arthroscopy.
Figures


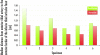
Similar articles
-
Ankle Arthroscopy: No-Distraction and Dorsiflexion Allows Advanced Techniques.Arthroscopy. 2019 Dec;35(12):3171-3172. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2019.10.013. Arthroscopy. 2019. PMID: 31785741
-
Distance Between the Anterior Distal Tibial Edge and the Anterior Tibial Artery in Distraction and Nondistraction During Anterior Ankle Arthroscopy: A Cadaveric Study.Foot Ankle Int. 2018 Jan;39(1):113-118. doi: 10.1177/1071100717732550. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Foot Ankle Int. 2018. PMID: 29073776
-
Effect of Ankle Position and Noninvasive Distraction on Arthroscopic Accessibility of the Distal Tibial Plafond.Foot Ankle Int. 2017 Oct;38(10):1152-1159. doi: 10.1177/1071100717717264. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Foot Ankle Int. 2017. PMID: 28741435
-
Advancements in ankle arthroscopy.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008 Nov;16(11):635-46. doi: 10.5435/00124635-200811000-00004. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008. PMID: 18978286 Review.
-
Arthroscopic Anatomy of the Ankle Joint.Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2016 Oct;33(4):467-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cpm.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2016. PMID: 27599433 Review.
Cited by
-
Response to: comment on "complications in ankle arthroscopy": anatomy, an important factor to avoid complications related to ankle arthroscopy.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013 Jul;21(7):1710-1. doi: 10.1007/s00167-012-2337-3. Epub 2013 Jan 5. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013. PMID: 23291789 No abstract available.
-
Clinical Outcomes After Arthroscopic Broström-Gould Procedure for Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability.Cureus. 2025 Mar 23;17(3):e81025. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81025. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40264622 Free PMC article.
-
Distraction-free ankle arthroscopy for anterolateral impingement.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014 Aug;24(6):1019-23. doi: 10.1007/s00590-013-1357-0. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014. PMID: 24220747
-
Accessibility to Talar Dome in Neutral Position, Dorsiflexion, or Noninvasive Distraction in Posterior Ankle Arthroscopy.Foot Ankle Int. 2019 Aug;40(8):978-986. doi: 10.1177/1071100719847134. Epub 2019 May 12. Foot Ankle Int. 2019. PMID: 31081369 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Visibility and Risk of Neurovascular Tissue Injury Between Portals in Needle Arthroscopy of the Anterior Ankle Joint: A Cadaveric Study.Orthop J Sports Med. 2023 Jun 2;11(6):23259671231174477. doi: 10.1177/23259671231174477. eCollection 2023 Jun. Orthop J Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 37332532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amendola A, Petrik J, Webster-Bogaert S. Ankle arthroscopy: outcome in 79 consecutive patients. Arthroscopy. 1996;12:565–573. - PubMed
-
- Andrews JR, Previte WJ, Carson WG. Arthroscopy of the ankle: technique and normal anatomy. Foot Ankle. 1985;6:29–33. - PubMed
-
- Aydin AT, Ozcanli H, Soyuncu Y, Dabak TK. A new noninvasive controlled intra-articular ankle distraction technique on a cadaver model. Arthroscopy. 2006;22:905e1–905e3. - PubMed
-
- Barber FA, Click J, Britt BT. Complications of ankle arthroscopy. Foot Ankle. 1990;10:263–266. - PubMed
-
- Bonnin M, Bouysset M. Arthroscopy of the ankle: analysis of results and indications on a series of 75 cases. Foot Ankle Int. 1999;20:744–751. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

