A capture coupling method for the covalent immobilization of hexahistidine tagged proteins for surface plasmon resonance
- PMID: 20217615
- PMCID: PMC3031178
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-60761-670-2_5
A capture coupling method for the covalent immobilization of hexahistidine tagged proteins for surface plasmon resonance
Abstract
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is a robust method to detect and quantify macromolecular interactions; however, to measure binding interactions, one component must be immobilized on a sensor surface. This is typically achieved using covalent immobilization via free amines or thiols, or noncovalent immobilization using high-affinity interactions such as biotin/streptavidin or antibody/antigen. In this chapter we describe a robust method to covalently immobilize His(6) fusion proteins on the sensor surface for SPR analysis.
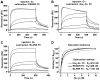
Figures


References
-
- Soundararajan M, Willard FS, Kimple AJ, Turnbull AP, Ball LJ, Schoch GA, Gileadi C, Fedorov OY, Dowler EF, Higman VA, Hutsell SQ, Sundstrom M, Doyle DA, Siderovski DP. Structural diversity in the RGS domain and its interaction with heterotrimeric G protein alpha-subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:6457–62. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Johnsson B, Lofas S, Lindquist G. Immobilization of proteins to a carboxymethyldextran-modified gold surface for biospecific interaction analysis in surface plasmon resonance sensors. Anal Biochem. 1991;198:268–77. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

