Xenobiology: a new form of life as the ultimate biosafety tool
- PMID: 20217844
- PMCID: PMC2909387
- DOI: 10.1002/bies.200900147
Xenobiology: a new form of life as the ultimate biosafety tool
Abstract
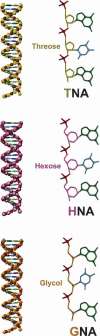
Synthetic biologists try to engineer useful biological systems that do not exist in nature. One of their goals is to design an orthogonal chromosome different from DNA and RNA, termed XNA for xeno nucleic acids. XNA exhibits a variety of structural chemical changes relative to its natural counterparts. These changes make this novel information-storing biopolymer "invisible" to natural biological systems. The lack of cognition to the natural world, however, is seen as an opportunity to implement a genetic firewall that impedes exchange of genetic information with the natural world, which means it could be the ultimate biosafety tool. Here I discuss, why it is necessary to go ahead designing xenobiological systems like XNA and its XNA binding proteins; what the biosafety specifications should look like for this genetic enclave; which steps should be carried out to boot up the first XNA life form; and what it means for the society at large.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Orthogonal Genetic Systems.Chembiochem. 2020 May 15;21(10):1408-1411. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201900725. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Chembiochem. 2020. PMID: 31889390
-
The structural diversity of artificial genetic polymers.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Feb 18;44(3):1007-21. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1472. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26673703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redesigning the Genetic Polymers of Life.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Feb 16;54(4):1056-1065. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00886. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 33533593
-
Compartmentalized Self-Tagging for In Vitro-Directed Evolution of XNA Polymerases.Curr Protoc Nucleic Acid Chem. 2014 Jun 24;57:9.9.1-18. doi: 10.1002/0471142700.nc0909s57. Curr Protoc Nucleic Acid Chem. 2014. PMID: 24961724 Review.
-
Xenobiology for the Biocontainment of Synthetic Organisms: Opportunities and Challenges.Life (Basel). 2024 Aug 10;14(8):996. doi: 10.3390/life14080996. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202738 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Computational Evaluation of Nucleotide Insertion Opposite Expanded and Widened DNA by the Translesion Synthesis Polymerase Dpo4.Molecules. 2016 Jun 23;21(7):822. doi: 10.3390/molecules21070822. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27347908 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic biology: mapping the scientific landscape.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34368. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034368. Epub 2012 Apr 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22539946 Free PMC article.
-
Bridging the gap: a roadmap to breaking the biological design barrier.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015 Jan 20;2:87. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2014.00087. eCollection 2014. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25654077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Directed evolution of artificial enzymes (XNAzymes) from diverse repertoires of synthetic genetic polymers.Nat Protoc. 2015 Oct;10(10):1625-42. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2015.104. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Nat Protoc. 2015. PMID: 26401917
-
From polymerase engineering to semi-synthetic life: artificial expansion of the central dogma.RSC Chem Biol. 2022 Aug 9;3(10):1173-1197. doi: 10.1039/d2cb00116k. eCollection 2022 Oct 5. RSC Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 36320892 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

