Promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through matrix metalloproteinase activation by epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulator Twist1
- PMID: 20219012
- PMCID: PMC3922390
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01052.x
Promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through matrix metalloproteinase activation by epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulator Twist1
Abstract
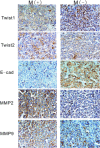
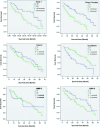
E-cadherin loss is a key biological mechanism in tumour invasion. As a main regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) mechanism-mediated invasion and metastasis, Twist1 plays an important role through its regulation of E-cadherin expression. However, whether or not Twist2 has the same function in tumour metastasis remains unclear. The purpose of this study is to investigate the expressions and different roles of Twist1 and Twist2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The expressions of Twist1 and Twist2 in HCC tissue were evaluated by immunohistochemical staining. The role of Twist1 and Twist2 in invasiveness was also evaluated in vitro by using HCC cell lines. Twist1 nuclear overexpression is found to be correlated with HCC metastasis, and its expression is negatively correlated with E-cadherin expression in human tissue. Twist2, a Twist1 homology protein, only expresses in the cytoplasm and shows no significant correlation with HCC metastasis. By ectopic transfection of Twist1 and Twist2 into the HCC cells, HepG2 and PLC, Twist1 is able to down-regulate E-cadherin expression and promote matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activation, specifically in MMP2 and MMP9. In functional assays, Twist1 is found to promote invasion in HepG2 and PLC cells, but the invasion ability of the groups is not affected Twist2. Our findings indicate that Twist1 induces HCC invasion via increased activity in MMPs, leading to poor clinical prognoses. The results of this study also demonstrate a novel cogitation in Twist2, which has no effect on HCC invasion and metastasis. Twist1 may contribute to HCC invasion and metastasis and may be used as a novel therapeutic target for the inhibition of HCC metastasis.
© 2011 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2011 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Kuper H, Ye W, Broome U, et al. The risk of liver and bile duct cancer in patients with chronic viral hepatitis, alcoholism, or cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2001;34:714–8. - PubMed
-
- El-Assal ON, Yamanoi A, SodaY, et al. Proposal of invasiveness score to predict recurrence and survival after curative hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Surgery. 1997;122:571–7. - PubMed
-
- Toyosaka A, Okamoto E, Mitsunobu M, et al. Intrahepatic metastases in hepatocellular carcinoma: evidence for spread via the portal vein as an efferent vessel. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996;91:1610–5. - PubMed
-
- Thiery JP, Sleeman JP. Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:131–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

