The development of drugs for treatment of sleeping sickness: a historical review
- PMID: 20219092
- PMCID: PMC2848007
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-3305-3-15
The development of drugs for treatment of sleeping sickness: a historical review
Abstract
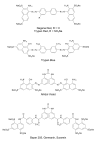
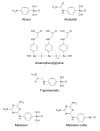
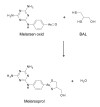
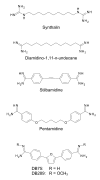
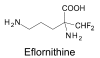
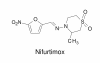
Only four drugs are available for the chemotherapy of human African trypanosomiasis or sleeping sickness; Suramin, pentamidine, melarsoprol and eflornithine. The history of the development of these drugs is well known and documented. suramin, pentamidine and melarsoprol were developed in the first half of the last century by the then recently established methods of medicinal chemistry. Eflornithine, originally developed in the 1970s as an anti-cancer drug, became a treatment of sleeping sickness largely by accident. This review summarises the developmental processes which led to these chemotherapies from the discovery of the first bioactive lead compounds to the identification of the final drugs.
Figures
References
-
- Molyneux DH, Pentreath V, Doua F. In: Manson's Tropical Diseases. 20. Cook GC, editor. London: W.B. Saunders; 1996. African trypanosomiasis in man; pp. 1171–1196.
-
- World Health Organization. Control of human African trypanosomiasis: a strategy for the African region. 2005. AFRO, AFR/RC55/11.
-
- World Health Organization. African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) World Health Organ Fact Sheet. 2006. p. 259.http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs259/en/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

