Specific effects of bortezomib against experimental malignant pleural effusion: a preclinical study
- PMID: 20219102
- PMCID: PMC2841124
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-56
Specific effects of bortezomib against experimental malignant pleural effusion: a preclinical study
Abstract
Background: We have previously shown that nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB activation of mouse Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) specifically promotes the induction of malignant pleural effusions (MPE) by these cells. In the present studies we hypothesized that treatment of immunocompetent mice with bortezomib tailored to inhibit cancer cell NF-kappaB activation and not proliferation specifically inhibits MPE formation by LLC cells.
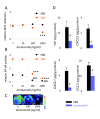
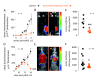
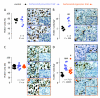
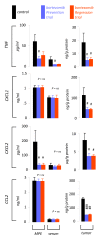
Results: Treatment of LLC cells with low concentrations of bortezomib (100 ng/ml) inhibited NF-kappaB activation and NF-kappaB-dependent transcription, but not cellular proliferation. Bortezomib treatment of immunocompetent C57BL/6 mice bearing LLC-induced subcutaneous tumors and MPEs significantly blocked tumor-specific NF-kappaB activation. However, bortezomib treatment did not impair subcutaneous LLC tumor growth, but was effective in limiting LLC-induced MPE. This specific effect was evidenced by significant reductions in effusion accumulation and the associated mortality and was observed with both preventive (beginning before MPE formation) and therapeutic (beginning after MPE establishment) bortezomib treatment. The favorable impact of bortezomib on MPE was associated with suppression of cardinal MPE-associated phenomena, such as inflammation, vascular hyperpermeability, and angiogenesis. In this regard, therapeutic bortezomib treatment had identical favorable results on MPE compared with preventive treatment, indicating that the drug specifically counteracts effusion formation.
Conclusions: These studies indicate that proteasome inhibition tailored to block NF-kappaB activation of lung adenocarcinoma specifically targets the effusion-inducing phenotype of this tumor. Although the drug has limited activity against advanced solid lung cancer, it may prove beneficial for patients with MPE.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha promotes malignant pleural effusion.Cancer Res. 2007 Oct 15;67(20):9825-34. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1064. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17942913
-
Bortezomib-enhanced radiosensitization through the suppression of radiation-induced nuclear factor-κB activity in human oral cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2013 Mar;42(3):935-44. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1786. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23340716
-
Anti-tumor activity of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in gastric cancer.Int J Oncol. 2011 Dec;39(6):1529-36. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2011.1141. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Int J Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21785822
-
Proteasome inhibition: a new approach for the treatment of malignancies.Bull Cancer. 2005 Nov;92(11):E61-6, 945-52. Bull Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16316823 Review. English, French.
-
The proteasome: a worthwhile target for the treatment of solid tumours?Eur J Cancer. 2007 May;43(7):1125-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2007.01.038. Epub 2007 Mar 26. Eur J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17379504 Review.
Cited by
-
Malignant pleural effusion: further translational research is crucial.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2012 Sep;1(3):167-9. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2012.09.06. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 25806178 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A modified experimental model of malignant pleural disease induced by lung Lewis carcinoma (LLC) cells.J Transl Med. 2015 Sep 15;13:302. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0662-2. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26373420 Free PMC article.
-
Malignant pleural effusion: from bench to bedside.Eur Respir Rev. 2016 Jun;25(140):189-98. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0019-2016. Eur Respir Rev. 2016. PMID: 27246596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment of a malignant pleural effusion mouse model: pathogenesis pathways.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2012 Sep;1(3):163-6. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2012.08.02. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 25806177 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Switching off malignant pleural effusion formation-fantasy or future?J Thorac Dis. 2015 Jun;7(6):1009-20. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2015.05.20. J Thorac Dis. 2015. PMID: 26150914 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sugiura S, Ando Y, Minami H, Ando M, Sakai S, Shimokata K. Prognostic value of pleural effusion in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1997;3:47–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

