Molecular advances in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
- PMID: 20219615
- PMCID: PMC2837604
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ackd.2010.01.002
Molecular advances in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
Abstract
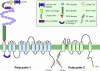
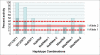
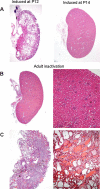
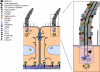
Autosomal dominant polycystic disease (ADPKD) is the most common form of inherited kidney disease that results in renal failure. The understanding of the pathogenesis of ADPKD has advanced significantly since the discovery of the 2 causative genes, PKD1 and PKD2. Dominantly inherited gene mutations followed by somatic second-hit mutations inactivating the normal copy of the respective gene result in renal tubular cyst formation that deforms the kidney and eventually impairs its function. The respective gene products, polycystin-1 and polycystin-2, work together in a common cellular pathway. Polycystin-1, a large receptor molecule, forms a receptor-channel complex with polycystin-2, which is a cation channel belonging to the TRP family. Both polycystin proteins have been localized to the primary cilium, a nonmotile microtubule-based structure that extends from the apical membrane of tubular cells into the lumen. Here we discuss recent insights in the pathogenesis of ADPKD including the genetics of ADPKD, the properties of the respective polycystin proteins, the role of cilia, and some cell-signaling pathways that have been implicated in the pathways related to PKD1 and PKD2.
2010 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Torres VE, Harris PC, Pirson Y. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet. 2007;369:1287–1301. - PubMed
-
- The European Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium The polycystic kidney disease 1 gene encodes a 14 kb transcript and lies within a duplicated region on chromosome 16. Cell. 1994;78:725. - PubMed
-
- The International Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium Polycystic kidney disease: the complete structure of the PKD1 gene and its protein. Cell. 1995;81:289–298. - PubMed
-
- Mochizuki T, Wu G, Hayashi T, Xenophontos SL, Veldhuisen B, Saris JJ, Reynolds DM, Cai Y, Gabow PA, Pierides A, et al. PKD2, a gene for polycystic kidney disease that encodes an integral membrane protein. Science. 1996;272:1339–1342. - PubMed
-
- Onuchic LF, Furu L, Nagasawa Y, Hou X, Eggermann T, Ren Z, Bergmann C, Senderek J, Esquivel E, Zeltner R, et al. PKHD1, the polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1 gene, encodes a novel large protein containing multiple immunoglobulin-like plexin-transcription-factor domains and parallel beta-helix 1 repeats. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002;70:1305–1317. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

