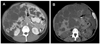
Isolated polycystic liver disease
- PMID: 20219621
- PMCID: PMC2837599
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ackd.2009.12.005
Isolated polycystic liver disease
Abstract
Isolated polycystic liver disease (PCLD) is an autosomal dominant disease with genetic and clinical heterogeneity. Apart from liver cysts, it exhibits few extrahepatic manifestations, and the majority of patients with this condition are asymptomatic or subclinical. However, a small fraction of these patients develop acute liver cyst-related complications and/or massive cystic liver enlargement, causing morbidity and mortality. Currently, the management for symptomatic PCLD is centered on palliating symptoms and treating complications.
2010 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polycystic liver: clinical characteristics of patients with isolated polycystic liver disease compared with patients with polycystic liver and autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Liver Int. 2008 Feb;28(2):264-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2007.01595.x. Epub 2007 Oct 9. Liver Int. 2008. PMID: 17927714
-
Polycystic liver disease: an overview of pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and management.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014 May 1;9:69. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-9-69. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014. PMID: 24886261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intravascular embolization therapy in patients with enlarged polycystic liver.Am J Kidney Dis. 2014 Jun;63(6):937-44. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.01.422. Epub 2014 Mar 4. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014. PMID: 24602778
-
Polycystic Kidney/Liver Disease.Clin Liver Dis. 2022 May;26(2):229-243. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2022.01.009. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Clin Liver Dis. 2022. PMID: 35487607 Review.
-
New therapeutic option for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease patients with enlarged kidney and liver.Ther Apher Dial. 2006 Aug;10(4):333-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-9987.2006.00386.x. Ther Apher Dial. 2006. PMID: 16911186
Cited by
-
Imaging features and management of focal liver lesions.World J Radiol. 2024 Jun 28;16(6):139-167. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i6.139. World J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38983841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Congenital and hereditary cystic diseases of the abdomen.Insights Imaging. 2020 Aug 5;11(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s13244-020-00898-z. Insights Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32757136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polycystic liver disease.BMJ Case Rep. 2014 Jan 17;2014:bcr2013202003. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2013-202003. BMJ Case Rep. 2014. PMID: 24443335 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for a "Pathogenic Triumvirate" in Congenital Hepatic Fibrosis in Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:4918798. doi: 10.1155/2016/4918798. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27891514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term results of liver transplantation for polycystic liver disease: Single-center experience in China.Exp Ther Med. 2019 May;17(5):4183-4189. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7449. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31007749 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Melnick PJ. Polycystic liver; analysis of seventy cases. AMA Arch Pathol. 1955;59(2):162–172. - PubMed
-
- Moschcowitz E. Non-parasitic cysts (congenital) of the liver, with a study of aberrant bile ducts. The American Journal of the Medical Sciences. 1906;131(4):674–699.
-
- Feldman M. Polycystic disease of the liver. Am J Gastroenterol. 1958;29(1):83–86. - PubMed
-
- Berrebi G, Erickson RP, Marks BW. Autosomal dominant polycystic liver disease: a second family. Clin Genet. 1982;21(5):342–347. - PubMed
-
- Tahvanainen P, Tahvanainen E, Reijonen H, Halme L, Kaariainen H, Hockerstedt K. Polycystic liver disease is genetically heterogeneous: clinical and linkage studies in eight Finnish families. J Hepatol. 2003;38(1):39–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical