Phosphodiesterase type 1 inhibition improves learning in rats exposed to alcohol during the third trimester equivalent of human gestation
- PMID: 20219634
- PMCID: PMC2847631
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.02.046
Phosphodiesterase type 1 inhibition improves learning in rats exposed to alcohol during the third trimester equivalent of human gestation
Abstract
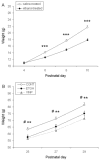
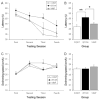
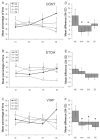
Deficits in learning and memory have been extensively observed in animal models of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD). Here we use the Morris maze to test whether vinpocetine, a phosphodiesterase type 1 inhibitor, restores learning performance in rats exposed to alcohol during the third trimester equivalent of human gestation. Long Evans rats received ethanol (5g/kg i.p.) or saline on alternate days from postnatal day (P) 4 to P10. Two weeks later (P25), the latency to find a hidden platform was evaluated (2 trials per day spaced at 40-min inter-trial intervals) during 4 consecutive days. Vinpocetine treatment started on the first day of behavioral testing: animals received vinpocetine (20mg/kg i.p.) or vehicle solution every other day until the end of behavioral procedures. Early alcohol exposure significantly affected the performance to find the hidden platform. The average latency of ethanol-exposed animals was significantly higher than that observed for the control group. Treatment of alcohol-exposed animals with vinpocetine restored their performance to control levels. Our results show that inhibition of PDE1 improves learning and memory deficits in rats early exposed to alcohol and provide evidence for the potential therapeutic use of vinpocetine in FASD.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acute administration of vinpocetine, a phosphodiesterase type 1 inhibitor, ameliorates hyperactivity in a mice model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011 Dec 1;119(1-2):81-7. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.05.024. Epub 2011 Sep 9. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011. PMID: 21689896
-
Early ethanol exposure and vinpocetine treatment alter learning- and memory-related proteins in the rat hippocampus and prefrontal cortex.J Neurosci Res. 2017 May;95(5):1204-1215. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23894. Epub 2016 Sep 10. J Neurosci Res. 2017. PMID: 27614144
-
The protective and therapeutic effects of vinpocetine, a PDE1 inhibitor, on oxidative stress and learning and memory impairment induced by an intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection of amyloid beta (aβ) peptide.Behav Brain Res. 2020 Apr 6;383:112512. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2020.112512. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Behav Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 31991177
-
Early alcohol exposure disrupts visual cortex plasticity in mice.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2012 Aug;30(5):351-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2012.05.001. Epub 2012 May 14. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22617459 Free PMC article.
-
NTP Developmental and Reproductive Toxicity Technical Report on the Prenatal Development Studies of Vinpocetine (CASRN 42971-09-5) in Sprague Dawley (Hsd:Sprague Dawley® SD®) Rats and New Zealand White (Hra:Nzw Spf) Rabbits (Gavage Studies): DART Report 03 [Internet].Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2020 Jun. Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2020 Jun. PMID: 32716616 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic utility of phosphodiesterase type I inhibitors in neurological conditions.Front Neurosci. 2011 Feb 18;5:21. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2011.00021. eCollection 2011. Front Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21373359 Free PMC article.
-
Neurological and psychiatric sequelae of developmental exposure to antiepileptic drugs.Front Neurol. 2012 Dec 27;3:182. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2012.00182. eCollection 2012. Front Neurol. 2012. PMID: 23293628 Free PMC article.
-
Role of phosphodiesterase 1 in the pathophysiology of diseases and potential therapeutic opportunities.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Oct;226:107858. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107858. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33895190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developmental effects of antiepileptic drugs and the need for improved regulations.Neurology. 2016 Jan 19;86(3):297-306. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002119. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Neurology. 2016. PMID: 26519545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphodiesterase-1b (Pde1b) knockout mice are resistant to forced swim and tail suspension induced immobility and show upregulation of Pde10a.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Jun;234(12):1803-1813. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4587-8. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28337525
References
-
- Burd L, Cotsonas-Hassler TM, Martsolf JT, Kerbeshian J. Recognition and management of fetal alcohol syndrome. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2003;25:681–688. - PubMed
-
- Burden MJ, Jacobson SW, Sokol RJ, Jacobson JL. Effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on attention and working memory at 7.5 years of age. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005;29:443–452. - PubMed
-
- Mattson SN, Riley EP. A review of the neurobehavioral deficits in children with fetal alcohol syndrome or prenatal exposure to alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998;22:279–294. - PubMed
-
- Uecker A, Nadel L. Spatial locations gone awry: Object and spatial memory deficits in children with fetal alcohol syndrome. Neuropsychologia. 1996;34:209–223. - PubMed
-
- Harris SR, MacKay LL, Osborn JA. Autistic behaviors in offspring of mothers abusing alcohol and other drugs: a series of case reports. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1995;19:660–665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

