Exercise and time-dependent benefits to learning and memory
- PMID: 20219647
- PMCID: PMC2857396
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.02.050
Exercise and time-dependent benefits to learning and memory
Abstract
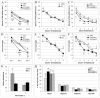
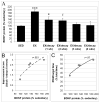
While it is well established that exercise can improve cognitive performance, it is unclear how long these benefits endure after exercise has ended. Accordingly, the effects of voluntary exercise on cognitive function and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) protein levels, a major player in the mechanisms governing the dynamics of memory formation and storage, were assessed immediately after a 3-week running period, or after a 1-week or 2-week delay following the exercise period. All exercised mice showed improved performance on the radial arm water maze relative to sedentary animals. Unexpectedly, fastest acquisition (fewest errors and shortest latency) occurred in animals trained following a 1-week delay, while best memory performance in the probe trial was observed in those trained immediately after the exercise period. Assessment of the time course of hippocampal BDNF availability following exercise revealed significant elevations of BDNF immediately after the exercise period (186% of sedentary levels) and at 1 and 2 weeks after exercise ended, with levels returning to baseline by 3-4 weeks. BDNF protein levels showed a positive correlation with cognitive improvement in radial water maze training and with memory performance on day 4, supporting the idea that BDNF availability contributes to the time-dependent cognitive benefits of exercise revealed in this study. Overall, this novel approach assessing the temporal endurance of cognitive and biochemical effects of exercise unveils new concepts in the exercise-learning field, and reveals that beneficial effects of exercise on brain plasticity continue to evolve even after exercise has ended.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott RD, White LR, Ross GW, Masaki KH, Curb JD, Petrovitch H. Walking and dementia in physically capable elderly men. Jama. 2004;292:1447–1453. - PubMed
-
- Alamed J, Wilcock DM, Diamond DM, Gordon MN, Morgan D. Two-day radial-arm water maze learning and memory task; robust resolution of amyloid-related memory deficits in transgenic mice. Nature protocols. 2006;1:1671–1679. - PubMed
-
- Bekinschtein P, Cammarota M, Izquierdo I, Medina JH. BDNF and memory formation and storage. Neuroscientist. 2008a;14:147–156. - PubMed
-
- Berchtold NC, Chinn G, Chou M, Kesslak JP, Cotman CW. Exercise primes a molecular memory for brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein induction in the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience. 2005;133:853–861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

