Migration of marrow stromal cells in response to sustained release of stromal-derived factor-1alpha from poly(lactide ethylene oxide fumarate) hydrogels
- PMID: 20219655
- PMCID: PMC2859691
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.12.063
Migration of marrow stromal cells in response to sustained release of stromal-derived factor-1alpha from poly(lactide ethylene oxide fumarate) hydrogels
Abstract
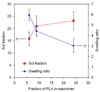
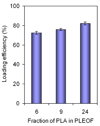
Stromal derived factor-1alpha (SDF-1alpha) is an important chemokine in stem cell trafficking and plays a critical role in the homing of bone marrow stromal (BMS) cells. However, its use in tissue regeneration is limited by its relatively short half-life and the time-dependent nature of cell homing to the site of injury. The objective of this work was to investigate the release characteristics of SDF-1alpha from degradable poly(lactide ethylene oxide fumarate) (PLEOF) hydrogels and to determine the effect of sustained release of SDF-1alpha on migration of BMS cells. Three PLEOF hydrogels with poly(l-lactide) (PLA) fractions of 6%, 9%, and 24% by weight were synthesized. After the addition of chemokine, the polymerizing mixture was crosslinked to produce SDF-1alpha loaded PLEOF hydrogels. The hydrogels were characterized with respect to sol fraction, water uptake, degradation, SDF-1alpha loading efficiency and release kinetics, and migration rate of bone marrow stromal (BMS) cells. The more hydrophilic hydrogels with 6% and 9% PLA fraction had a pronounced burst release followed by a period of sustained release by diffusion for 21 days. The more hydrophobic hydrogel with 24% PLA fraction had a less pronounced burst release and displayed a slow but constant release by diffusion between days 1 and 9 followed by a fast release by diffusion-degradation from days 9 to 18. The fraction of active SDF-1alpha released from 6%, 9%, and 24% hydrogels after 21 days was 34.3%, 32.3%, and 35.8%, respectively. The migration of BMS cells in response to time-released SDF-1alpha closely followed the protein release kinetics from the hydrogels. The biodegradable PLEOF hydrogel may potentially be useful as a delivery matrix for sustained release of SDF-1alpha in the proliferative phase of healing for recruitment of progenitor cells in tissue engineering applications.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Abbott JD, Huang Y, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha plays a critical role in stem cell recruitment to the heart after myocardial infarction but is not sufficient to induce homing in the absence of injury. Circulation. 2004;110(21):3300–3305. - PubMed
-
- Bladergroen BA, Siebum B, et al. In vivo recruitment of hematopoietic cells using stromal cell-derived factor 1 alpha-loaded heparinized three-dimensional collagen scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 2009;15(7):1591–1599. - PubMed
-
- Bussolati O, Belletti S, et al. Characterization of apoptotic phenomena induced by treatment with l-asparaginase in NIH3T3 cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1995;220(2):283–291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

