Minireview: beta-cell replacement therapy for diabetes in the 21st century: manipulation of cell fate by directed differentiation
- PMID: 20219891
- PMCID: PMC2940465
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0311
Minireview: beta-cell replacement therapy for diabetes in the 21st century: manipulation of cell fate by directed differentiation
Abstract
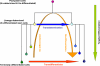
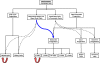
Pancreatic beta-cell failure underlies type 1 diabetes; it also contributes in an essential way to type 2 diabetes. beta-Cell replacement is an important component of any cure for diabetes. The current options of islet and pancreas transplantation are not satisfactory as definitive forms of therapy. Here, we review strategies for induced de novo pancreatic beta-cell formation, which depend on the targeted differentiation of cells into pancreatic beta-cells. With this objective in mind, one can manipulate the fate of three different types of cells: 1) from terminally differentiated cells, e.g. exocrine pancreatic cells, into beta-cells; 2) from multipotent adult stem cells, e.g. hepatic oval cells, into pancreatic islets; and 3) from pluripotent stem cells, e.g. embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells, into beta-cells. We will examine the pros and cons of each strategy as well as the hurdles that must be overcome before these approaches to generate new beta-cells will be ready for clinical application.
Figures
Similar articles
-
How to make pancreatic beta cells--prospects for cell therapy in diabetes.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2005 Oct;16(5):524-9. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2005.07.005. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2005. PMID: 16084716 Review.
-
Pluripotent stem cells, a potential source of beta-cells for diabetes therapy.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2010 Apr;11(4):417-25. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20336589 Review.
-
Stem cells and diabetes treatment.APMIS. 2005 Nov-Dec;113(11-12):858-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2005.apm_418.x. APMIS. 2005. PMID: 16480455 Review.
-
[From stem cells to functional beta cells in type 1 diabetes].Ugeskr Laeger. 2010 Sep 20;172(38):2608-12. Ugeskr Laeger. 2010. PMID: 20920405 Review. Danish.
-
How to make insulin-producing pancreatic β cells for diabetes treatment.Sci China Life Sci. 2017 Mar;60(3):239-248. doi: 10.1007/s11427-016-0211-3. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Sci China Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27796637 Review.
Cited by
-
ROCK1 reduces mitochondrial content and irisin production in muscle suppressing adipocyte browning and impairing insulin sensitivity.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 14;6:29669. doi: 10.1038/srep29669. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27411515 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative-proteomic comparison of alpha and Beta cells to uncover novel targets for lineage reprogramming.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 23;9(4):e95194. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095194. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24759943 Free PMC article.
-
The temporal and hierarchical control of transcription factors-induced liver to pancreas transdifferentiation.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 4;9(2):e87812. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087812. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24504462 Free PMC article.
-
Demethylation of induced pluripotent stem cells from type 1 diabetic patients enhances differentiation into functional pancreatic β cells.J Biol Chem. 2017 Aug 25;292(34):14066-14079. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.784280. Epub 2017 Mar 30. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28360105 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of islet-like cells from mouse gall bladder by direct ex vivo reprogramming.Stem Cell Res. 2013 Jul;11(1):503-15. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2013.02.005. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Stem Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23562832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases 2008 National Diabetes Statistics, 2007 fact sheet. Bethesda, MD: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health
-
- Narayan KM, Boyle JP, Geiss LS, Saaddine JB, Thompson TJ 2006 Impact of recent increase in incidence on future diabetes burden: U.S., 2005–2050. Diabetes Care 29:2114–2116 - PubMed
-
- Narayan KM, Boyle JP, Thompson TJ, Sorensen SW, Williamson DF 2003 Lifetime risk for diabetes mellitus in the United States. JAMA 290:1884–1890 - PubMed
-
- Boyle JP, Honeycutt AA, Narayan KM, Hoerger TJ, Geiss LS, Chen H, Thompson TJ 2001 Projection of diabetes burden through 2050: impact of changing demography and disease prevalence in the U.S. Diabetes Care 24:1936–1940 - PubMed
-
- Engelgau MM, Geiss LS, Saaddine JB, Boyle JP, Benjamin SM, Gregg EW, Tierney EF, Rios-Burrows N, Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Imperatore G, Narayan KM 2004 The evolving diabetes burden in the United States. Ann Intern Med 140:945–950 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

