Visualizing viral dissemination in the mouse nervous system, using a green fluorescent protein-expressing Borna disease virus vector
- PMID: 20219925
- PMCID: PMC2863799
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00098-10
Visualizing viral dissemination in the mouse nervous system, using a green fluorescent protein-expressing Borna disease virus vector
Abstract
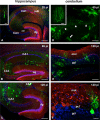
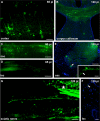
Borna disease virus (BDV) frequently persists in the brain of infected animals. To analyze viral dissemination in the mouse nervous system, we generated a mouse-adapted virus that expresses green fluorescent protein (GFP). This viral vector supported GFP expression for up to 150 days and possessed an extraordinary staining capacity, visualizing complete dendritic arbors as well as individual axonal fibers of infected neurons. GFP-positive cells were first detected in cortical areas from where the virus disseminated through the entire central nervous system (CNS). Late in infection, GFP expression was found in the sciatic nerve, demonstrating viral spread from the central to the peripheral nervous system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurological diseases and viral dynamics in the brains of neonatally borna disease virus-infected gerbils.Virology. 2001 Mar 30;282(1):65-76. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.0813. Virology. 2001. PMID: 11259191
-
[The neuropathogenesis of Borna disease virus infection].Nihon Rinsho. 2001 Aug;59(8):1605-13. Nihon Rinsho. 2001. PMID: 11519168 Review. Japanese.
-
Bornavirus and the brain.J Infect Dis. 2002 Dec 1;186 Suppl 2:S241-7. doi: 10.1086/344936. J Infect Dis. 2002. PMID: 12424704 Review.
-
Generation of a non-transmissive Borna disease virus vector lacking both matrix and glycoprotein genes.Microbiol Immunol. 2017 Sep;61(9):380-386. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12505. Microbiol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28776750
-
Rabies and borna disease. A comparative pathogenetic study of two neurovirulent agents.Lab Invest. 1993 Mar;68(3):285-95. Lab Invest. 1993. PMID: 8450648
Cited by
-
Avian Bornavirus Research-A Comprehensive Review.Viruses. 2022 Jul 11;14(7):1513. doi: 10.3390/v14071513. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35891493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic stability of the open reading frame 2 (ORF2) of borna disease virus 1 (BoDV-1) distributed in cattle in Hokkaido.J Vet Med Sci. 2021 Oct 2;83(10):1526-1533. doi: 10.1292/jvms.21-0155. Epub 2021 Aug 13. J Vet Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34393150 Free PMC article.
-
Word recognition memory and serum levels of Borna disease virus specific circulating immune complexes in obsessive-compulsive disorder.BMC Psychiatry. 2022 Sep 8;22(1):597. doi: 10.1186/s12888-022-04208-3. BMC Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36076225 Free PMC article.
-
A novel borna disease virus vector system that stably expresses foreign proteins from an intercistronic noncoding region.J Virol. 2011 Dec;85(23):12170-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05554-11. Epub 2011 Sep 21. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21937656 Free PMC article.
-
A novel porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus vector system that stably expresses enhanced green fluorescent protein as a separate transcription unit.Vet Res. 2013 Oct 31;44(1):104. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-44-104. Vet Res. 2013. PMID: 24176053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Celio, M. R. 1990. Calbindin D-28k and parvalbumin in the rat nervous system. Neuroscience 35:375-475. - PubMed
-
- de la Torre, J. C. 2002. Bornavirus and the brain. J. Infect. Dis. 186(Suppl. 2):S241-S247. - PubMed
-
- Herzog, S., C. Kompter, K. Frese, and R. Rott. 1984. Replication of Borna disease virus in rats: age-dependent differences in tissue distribution. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 173:171-177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

