Comprehensive analysis of Rhesus lymphocryptovirus microRNA expression
- PMID: 20219930
- PMCID: PMC2863793
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00110-10
Comprehensive analysis of Rhesus lymphocryptovirus microRNA expression
Abstract
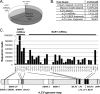
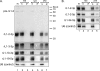
Rhesus lymphocryptovirus (rLCV) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) are closely related gammaherpesviruses that infect and cause disease in rhesus monkeys and humans, respectively. Thus, rLCV is an important model system for EBV pathogenesis. Both rLCV and EBV express microRNAs (miRNAs), several conserved in sequence and genomic location. We have applied deep sequencing technology to obtain an inventory of rLCV miRNA expression in latently rLCV-infected monkey B cells. Our data confirm the presence of all previously identified mature rLCV miRNAs and have resulted in the discovery of 21 new mature miRNAs arising from previously identified precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs), as well as two novel pre-miRNAs (rL1-34 and rL1-35) that together generate four new mature miRNAs. Thus, the total number of rLCV-encoded pre-miRNAs is 35 and the total number of rLCV mature miRNAs is 68, the most of any virus examined. The exact 5' and 3' ends of all mature rLCV miRNAs were pinpointed, many showing marked sequence and length heterogeneity that could modulate function. We further demonstrate that rLCV mature miRNAs associate with Argonaute proteins in rLCV-infected B cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evolutionary conservation of primate lymphocryptovirus microRNA targets.J Virol. 2014 Feb;88(3):1617-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02071-13. Epub 2013 Nov 20. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24257599 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Gammaherpesvirus Circular RNA Repertoires: Conserved and Unique Viral Circular RNAs.J Virol. 2019 Mar 5;93(6):e01952-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01952-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30567979 Free PMC article.
-
A global analysis of evolutionary conservation among known and predicted gammaherpesvirus microRNAs.J Virol. 2010 Jan;84(2):716-28. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01302-09. Epub 2009 Nov 4. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 19889779 Free PMC article.
-
Non-human Primate Lymphocryptoviruses: Past, Present, and Future.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:385-405. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_13. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428382 Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs as regulators in host immune responses.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 Apr 5;14(5):565-576. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.24562. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29805308 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The viral and cellular microRNA targetome in lymphoblastoid cell lines.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Jan;8(1):e1002484. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002484. Epub 2012 Jan 26. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22291592 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-encoded microRNAs.Virology. 2011 Mar 15;411(2):325-43. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.01.002. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Virology. 2011. PMID: 21277611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reciprocal inhibition between intracellular antiviral signaling and the RNAi machinery in mammalian cells.Cell Host Microbe. 2013 Oct 16;14(4):435-45. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.09.002. Epub 2013 Sep 26. Cell Host Microbe. 2013. PMID: 24075860 Free PMC article.
-
The porcine microRNA transcriptome response to transmissible gastroenteritis virus infection.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 17;10(3):e0120377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120377. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25781021 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Epstein-Barr virus miRNAome in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by deep sequencing.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 20;5(9):e12745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012745. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20862214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel, D. P. 2004. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281-297. - PubMed
-
- Beitzinger, M., L. Peters, J. Y. Zhu, E. Kremmer, and G. Meister. 2007. Identification of human microRNA targets from isolated argonaute protein complexes. RNA Biol. 4:76-84. - PubMed
-
- Blake, N. W., A. Moghaddam, P. Rao, A. Kaur, R. Glickman, Y. G. Cho, A. Marchini, T. Haigh, R. P. Johnson, A. B. Rickinson, and F. Wang. 1999. Inhibition of antigen presentation by the glycine/alanine repeat domain is not conserved in simian homologues of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1. J. Virol. 73:7381-7389. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

