Regulated transport of sulfate and oxalate by SLC26A2/DTDST
- PMID: 20219950
- PMCID: PMC2889644
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00004.2010
Regulated transport of sulfate and oxalate by SLC26A2/DTDST
Erratum in
- Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Feb;300(2):C383
Abstract
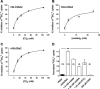
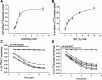
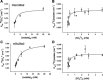
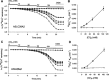
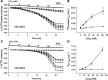
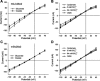
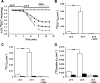
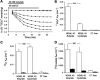
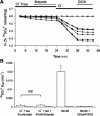
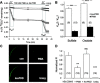
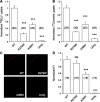
Nephrolithiasis in the Slc26a6(-/-) mouse is accompanied by 50-75% reduction in intestinal oxalate secretion with unchanged intestinal oxalate absorption. The molecular identities of enterocyte pathways for oxalate absorption and for Slc26a6-independent oxalate secretion remain undefined. The reported intestinal expression of SO(4)(2-) transporter SLC26A2 prompted us to characterize transport of oxalate and other anions by human SLC26A2 and mouse Slc26a2 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. We found that hSLC26A2-mediated [(14)C]oxalate uptake (K(1/2) of 0.65 +/- 0.08 mM) was cis-inhibited by external SO(4)(2-) (K(1/2) of 3.1 mM). hSLC26A2-mediated bidirectional oxalate/SO(4)(2-) exchange exhibited extracellular SO(4)(2-) K(1/2) of 1.58 +/- 0.44 mM for exchange with intracellular [(14)C]oxalate, and extracellular oxalate K(1/2) of 0.14 +/- 0.11 mM for exchange with intracellular (35)SO(4)(2-). Influx rates and K(1/2) values for mSlc26a2 were similar. hSLC26A2-mediated oxalate/Cl(-) exchange and bidirectional SO(4)(2-)/Cl(-) exchange were not detectably electrogenic. Both SLC26A2 orthologs exhibited nonsaturable extracellular Cl(-) dependence for efflux of intracellular [(14)C]oxalate, (35)SO(4)(2-), or (36)Cl(-). Rate constants for (36)Cl(-) efflux into extracellular Cl(-), SO(4)(2-), and oxalate were uniformly 10-fold lower than for oppositely directed exchange. Acidic extracellular pH (pH(o)) inhibited all modes of hSLC26A2-mediated anion exchange. In contrast, acidic intracellular pH (pH(i)) selectively activated exchange of extracellular Cl(-) for intracellular (35)SO(4)(2-) but not for intracellular (36)Cl(-) or [(14)C]oxalate. Protein kinase C inhibited hSLC26A2 by reducing its surface abundance. Diastrophic dysplasia mutants R279W and A386V of hSLC26A2 exhibited similar reductions in uptake of both (35)SO(4)(2-) and [(14)C]oxalate. A386V surface abundance was reduced, but R279W surface abundance was at wild-type levels.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional comparison of mouse slc26a6 anion exchanger with human SLC26A6 polypeptide variants: differences in anion selectivity, regulation, and electrogenicity.J Biol Chem. 2005 Mar 4;280(9):8564-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411703200. Epub 2004 Nov 17. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15548529
-
Solute carrier family 26 member a2 (Slc26a2) protein functions as an electroneutral SOFormula/OH-/Cl- exchanger regulated by extracellular Cl-.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 10;287(7):5122-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.297192. Epub 2011 Dec 21. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22190686 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Cl(-) regulates human SO4 (2-)/anion exchanger SLC26A1 by altering pH sensitivity of anion transport.Pflugers Arch. 2016 Aug;468(8):1311-32. doi: 10.1007/s00424-016-1823-8. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Pflugers Arch. 2016. PMID: 27125215 Free PMC article.
-
Essential roles of CFEX-mediated Cl(-)-oxalate exchange in proximal tubule NaCl transport and prevention of urolithiasis.Kidney Int. 2006 Oct;70(7):1207-13. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5001741. Epub 2006 Aug 2. Kidney Int. 2006. PMID: 16883319 Review.
-
The SLC26 gene family of multifunctional anion exchangers.Pflugers Arch. 2004 Feb;447(5):710-21. doi: 10.1007/s00424-003-1090-3. Epub 2003 May 21. Pflugers Arch. 2004. PMID: 12759755 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals differential nutrient absorption functions in human intestine.J Exp Med. 2020 Feb 3;217(2):e20191130. doi: 10.1084/jem.20191130. J Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 31753849 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency of rare allelic variation in candidate genes among individuals with low and high urinary calcium excretion.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 26;8(8):e71885. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071885. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23991001 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfate but not thiosulfate reduces calculated and measured urinary ionized calcium and supersaturation: implications for the treatment of calcium renal stones.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 25;9(7):e103602. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103602. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25061988 Free PMC article.
-
Substrate binding plasticity revealed by Cryo-EM structures of SLC26A2.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 29;15(1):3616. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48028-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38684689 Free PMC article.
-
SLC26 Anion Transporters.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024;283:319-360. doi: 10.1007/164_2023_698. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37947907 Review.
References
-
- Aronson PS, Giebisch G. Mechanisms of chloride transport in the proximal tubule. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 273: F179–F192, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Barmeyer C, Ye JH, Sidani S, Geibel J, Binder HJ, Rajendran VM. Characteristics of rat downregulated in adenoma (rDRA) expressed in HEK 293 cells. Pflügers Arch 454: 441–450, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Beauge L, DiPolo R. The squid axon Na/Ca2+ exchanger shows ping pong kinetics only when the Ca2+(i)-regulatory site is saturated. Cell Physiol Biochem 23: 37–42, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Burckhardt BC, Fromter E. Pathways of NH3/NH4+ permeation across Xenopus laevis oocyte cell membrane. Pflügers Arch 420: 83–86, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Chapman JM, Karniski LP. Protein localization of SLC26A2 (DTDST) in rat kidneys (Abstract). FASEB J 21: 937. 27, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

