Interaction of the double-strand break repair kinase DNA-PK and estrogen receptor-alpha
- PMID: 20219974
- PMCID: PMC2861619
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-08-0724
Interaction of the double-strand break repair kinase DNA-PK and estrogen receptor-alpha
Abstract
Estrogens are suggested to play a role in the development and progression of proliferative diseases such as breast cancer. Like other steroid hormone receptors, the estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha) is a substrate of protein kinases, and phosphorylation has profound effects on its function and activity. Given the importance of DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) for DNA repair, cell cycle progression, and survival, we hypothesized that it modulates ERalpha signaling. Here we show that, upon estrogen stimulation, DNA-PK forms a complex with ERalpha in a breast cancer cell line (MELN). DNA-PK phosphorylates ERalpha at Ser-118. Phosphorylation resulted in stabilization of ERalpha protein as inhibition of DNA-PK resulted in its proteasomal degradation. Activation of DNA-PK by double-strand breaks or its inhibition by siRNA technology demonstrated that estrogen-induced ERalpha activation and cell cycle progression is, at least, partially dependent on DNA-PK.
Figures
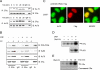

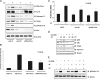
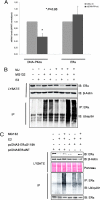
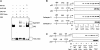
References
-
- Anderson C. W., Lees-Miller S. P. The nuclear serine/threonine protein kinase DNA-PK. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 1992;2:283–314. - PubMed
-
- Arnold S. F., Obourn J. D., Yudt M. R., Carter T. H., Notides A. C. In vivo and in vitro phosphorylation of the human estrogen receptor. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995;52:159–171. - PubMed
-
- Augereau P., Miralles F., Cavailles V., Gaudelet C., Parker M., Rochefort H. Characterization of the proximal estrogen-responsive element of human cathepsin D gene. Mol. Endocrinol. 1994;8:693–703. - PubMed
-
- Blunt T., et al. Defective DNA-dependent protein kinase activity is linked to V(D)J recombination and DNA repair defects associated with the murine scid mutation. Cell. 1995;80:813–823. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

