Dissecting the M phase-specific phosphorylation of serine-proline or threonine-proline motifs
- PMID: 20219976
- PMCID: PMC2861607
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-06-0486
Dissecting the M phase-specific phosphorylation of serine-proline or threonine-proline motifs
Abstract
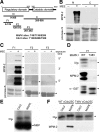
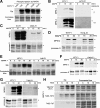
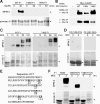
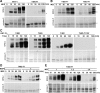
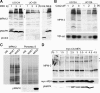
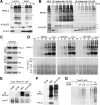
M phase induction in eukaryotic cell cycles is associated with a burst of protein phosphorylation, primarily at serine or threonine followed by proline (S/TP motif). The mitotic phosphoprotein antibody MPM-2 recognizes a significant subset of mitotically phosphorylated S/TP motifs; however, the required surrounding sequences of and the key kinases that phosphorylate these S/TP motifs remain to be determined. By mapping the mitotic MPM-2 epitopes in Xenopus Cdc25C and characterizing the mitotic MPM-2 epitope kinases in Xenopus oocytes and egg extracts, we have determined that phosphorylation of TP motifs that are surrounded by hydrophobic residues at both -1 and +1 positions plays a dominant role in M phase-associated burst of MPM-2 reactivity. Although mitotic Cdk and MAPK may phosphorylate subsets of these motifs that have a basic residue at the +2 position and a proline residue at the -2 position, respectively, the majority of these motifs that are preferentially phosphorylated in mitosis do not have these features. The M phase-associated burst of MPM-2 reactivity can be induced in Xenopus oocytes and egg extracts in the absence of MAPK or Cdc2 activity. These findings indicate that the M phase-associated burst of MPM-2 reactivity represents a novel type of protein phosphorylation in mitotic regulation.
Figures

References
-
- Alvarez E., Northwood I. C., Gonzalez F. A., Latour D. A., Seth A., Abate C., Curran T., Davis R. J. Pro-Leu-Ser/Thr-Pro is a consensus primary sequence for substrate protein phosphorylation. Characterization of the phosphorylation of c-myc and c-jun proteins by an epidermal growth factor receptor threonine 669 protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:15277–15285. - PubMed
-
- Brittle A. L., Ohkura H. Centrosome maturation: Aurora lights the way to the poles. Curr. Biol. 2005;15:R880–R882. - PubMed
-
- Campbell L. E., Proud C. G. Differing substrate specificities of members of the DYRK family of arginine-directed protein kinases. FEBS Lett. 2002;510:31–36. - PubMed
-
- Cano E., Mahadevan L. C. Parallel signal processing among mammalian MAPKs. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995;20:117–122. - PubMed
-
- Che S., El-Hodiri H. M., Wu C. F., Nelman-Gonzalez M., Weil M. M., Etkin L. D., Clark R. B., Kuang J. Identification and cloning of xp95, a putative signal transduction protein in Xenopus oocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:5522–5531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

