Glycinergic pacemaker neurons in preBötzinger complex of neonatal mouse
- PMID: 20219997
- PMCID: PMC2947441
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3040-09.2010
Glycinergic pacemaker neurons in preBötzinger complex of neonatal mouse
Abstract
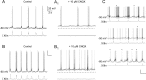
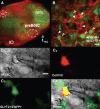
The preBötzinger complex (preBötC) is essential for normal respiratory rhythm generation in rodents, for which the underlying mechanisms remain unknown. Excitatory preBötC pacemaker neurons are proposed to be necessary for rhythm generation. Here we report the presence of a population of preBötC glycinergic pacemaker neurons. We used rhythmic in vitro transverse slice preparations from transgenic mice where neurons expressing the glycine transporter 2 (GlyT2) gene coexpress enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP). We combined epifluorescence and whole-cell patch-clamp recording to study preBötC EGFP-labeled, i.e., glycinergic, inspiratory-modulated neurons with pacemaker properties. We defined glycinergic pacemaker neurons as those preBötC EGFP neurons that exhibited the following: (1) ectopic bursting in rhythmic slices when depolarized during their normally silent period and (2) bursting when depolarized in nonrhythmic slices (following AMPA receptor blockade). Forty-two percent of EGFP-labeled neurons were inspiratory (n = 48 of 115), of which 23% (n = 11 of 48 inspiratory; 10% of the total recorded) were pacemakers. We conclude that there is a population of preBötC inspiratory-modulated glycinergic, presumably inhibitory, pacemaker neurons that constitute a substantial fraction of all preBötC pacemaker neurons. These findings challenge contemporary models for respiratory rhythmogenesis that assume the excitatory nature of preBötC pacemaker neurons. Testable and nontrivial predictions of the functional role of excitatory and inhibitory pacemaker neurons need to be proposed and the necessary experiments performed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibitory Subpopulations in preBötzinger Complex Play Distinct Roles in Modulating Inspiratory Rhythm and Pattern.J Neurosci. 2024 Jun 19;44(25):e1928232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1928-23.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38729762 Free PMC article.
-
GABAergic and glycinergic synapses onto neurokinin-1 receptor-immunoreactive neurons in the pre-Bötzinger complex of rats: light and electron microscopic studies.Eur J Neurosci. 2002 Sep;16(6):1058-66. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2002.02163.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12383234
-
Optogenetic perturbation of preBötzinger complex inhibitory neurons modulates respiratory pattern.Nat Neurosci. 2015 Mar;18(3):408-14. doi: 10.1038/nn.3938. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Nat Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25643296 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory Rhythm Generation: The Whole Is Greater Than the Sum of the Parts.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1015:147-161. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-62817-2_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29080026 Review.
-
PreBötzinger complex and pacemaker neurons: hypothesized site and kernel for respiratory rhythm generation.Annu Rev Physiol. 1998;60:385-405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.60.1.385. Annu Rev Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9558470 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural-functional properties of identified excitatory and inhibitory interneurons within pre-Botzinger complex respiratory microcircuits.J Neurosci. 2013 Feb 13;33(7):2994-3009. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4427-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23407957 Free PMC article.
-
Brainstem respiratory networks: building blocks and microcircuits.Trends Neurosci. 2013 Mar;36(3):152-62. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2012.11.004. Epub 2012 Dec 17. Trends Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23254296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
When norepinephrine becomes a driver of breathing irregularities: how intermittent hypoxia fundamentally alters the modulatory response of the respiratory network.J Neurosci. 2014 Jan 1;34(1):36-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3644-12.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24381266 Free PMC article.
-
Emergent Elements of Inspiratory Rhythmogenesis: Network Synchronization and Synchrony Propagation.Neuron. 2020 May 6;106(3):482-497.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.02.005. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Neuron. 2020. PMID: 32130872 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Subpopulations in preBötzinger Complex Play Distinct Roles in Modulating Inspiratory Rhythm and Pattern.J Neurosci. 2024 Jun 19;44(25):e1928232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1928-23.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38729762 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bianchi AL, Denavit-Saubié M, Champagnat J. Central control of breathing in mammals: neuronal circuitry, membrane properties, and neurotransmitters. Physiol Rev. 1995;75:1–45. - PubMed
-
- Brockhaus J, Ballanyi K. Synaptic inhibition in the isolated respiratory network of neonatal rats. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10:3823–3839. - PubMed
-
- Büsselberg D, Bischoff AM, Paton JF, Richter DW. Reorganisation of respiratory network activity after loss of glycinergic inhibition. Pflugers Arch. 2001;441:444–449. - PubMed
-
- Butera RJ, Jr, Rinzel J, Smith JC. Models of respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Bötzinger complex. I. Bursting pacemaker neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1999a;82:382–397. - PubMed
-
- Butera RJ, Jr, Rinzel J, Smith JC. Models of respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Bötzinger complex. II. Populations of coupled pacemaker neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1999b;82:398–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
