An on-line imitative test of speech-pattern contrast perception (OlimSpac): developmental effects in normally hearing children
- PMID: 20220029
- PMCID: PMC3031863
- DOI: 10.1044/1092-4388(2009/08-0260)
An on-line imitative test of speech-pattern contrast perception (OlimSpac): developmental effects in normally hearing children
Abstract
Purpose: The goal was to assess the effects of maturation and phonological development on performance, by normally hearing children, on an imitative test of auditory capacity (On-Line Imitative Test of Speech-Pattern Contrast Perception [OlimSpac]; Boothroyd, Eisenberg, & Martinez, 2006; Eisenberg, Martinez, & Boothroyd, 2003, 2007).
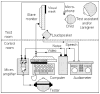
Method: Thirty-four hearing children (aged between 1;8 [years;months] and 6;7) were asked to imitate nonword utterances. Responses were evaluated by a blinded listener in an 8-alternative forced-choice task, giving information on the children's ability to convey, by imitation, information about 6 binary phonemic contrasts.
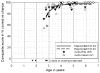
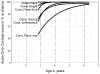
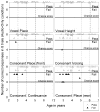
Results: Four children declined participation. Among 30 children aged 2;7 or older, performance improved significantly with age and varied with contrast. All children 3 years of age or older attained passing scores (7 or 8 correct responses in 8 binary trials) on at least 5 of the 6 contrasts. Post-alveolar consonant place was the contrast most often failed.
Conclusions: When evaluated on a pass/fail basis, normally hearing children 3 years of age or older are likely to demonstrate auditory perception of most phonemic contrasts using this imitative test. Phonological development and other task-related factors have only a modest effect on performance by normally hearing children after 3 years of age. The effects of hearing loss, hearing age, sensory assistance, and listening experience in children with hearing loss remain to be determined.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Relationships between speech perception abilities and spoken language skills in young children with hearing loss.Int J Audiol. 2009 May;48(5):248-59. doi: 10.1080/14992020802607423. Int J Audiol. 2009. PMID: 19842800 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of an on-line implementation of the Imitative test of Speech Pattern Contrast perception (IMSPAC).J Am Acad Audiol. 2003;14(2):72-83. doi: 10.3766/jaaa.14.2.3. J Am Acad Audiol. 2003. PMID: 12830843
-
Relationships among speech perception, production, language, hearing loss, and age in children with impaired hearing.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2001 Apr;44(2):264-85. doi: 10.1044/1092-4388(2001/022). J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2001. PMID: 11324650
-
Auditory Perception and Production of Speech Feature Contrasts by Pediatric Implant Users.Ear Hear. 2015 Nov-Dec;36(6):653-63. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000181. Ear Hear. 2015. PMID: 26035142
-
Current state of knowledge: speech recognition and production in children with hearing impairment.Ear Hear. 2007 Dec;28(6):766-72. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0b013e318157f01f. Ear Hear. 2007. PMID: 17982364 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Early Acoustic Hearing on Speech Perception and Language for Pediatric Cochlear Implant Recipients.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2019 Sep 20;62(9):3620-3637. doi: 10.1044/2019_JSLHR-H-18-0255. Epub 2019 Sep 13. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2019. PMID: 31518517 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive and linguistic sources of variance in 2-year-olds’ speech-sound discrimination: a preliminary investigation.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2014 Feb;57(1):308-26. doi: 10.1044/1092-4388(2013/12-0227). J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2014. PMID: 24023371 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Visual speech alters the discrimination and identification of non-intact auditory speech in children with hearing loss.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;94:127-137. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2017.01.009. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 28167003 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Segmental and Suprasegmental Speech Perception on Reading in Pediatric Cochlear Implant Recipients.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2022 Sep 12;65(9):3583-3594. doi: 10.1044/2022_JSLHR-22-00035. Epub 2022 Aug 24. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2022. PMID: 36001864 Free PMC article.
-
Preschoolers benefit from visually salient speech cues.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2015 Feb;58(1):135-50. doi: 10.1044/2014_JSLHR-H-13-0343. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2015. PMID: 25322336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blamey PJ, Sarant JZ, Paatsch LE, Barry JG, Bow CP, Wales RJ, Tooher R. Relationships among speech perception, production, language, hearing loss, and age in children with impaired hearing. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research. 2001;44:264–285. - PubMed
-
- Boothroyd A. Evaluation of speech production in the hearing-impaired: Some benefits of forced-choice testing. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research. 1985;28:185–196. - PubMed
-
- Boothroyd A. Auditory capacity of hearing-impaired children using hearing aids and cochlear implants: Issues of efficacy and assessment. Scandinavian Audiology. 1997a;26(Suppl 46):17–25. - PubMed
-
- Boothroyd A. Speech perception tests and hearing-impaired children. In: Plant G, Spens KE, editors. Profound deafness and speech communication. London, England: Whurr Publishers; 1997b. pp. 345–371.
-
- Boothroyd A. Evaluating the efficacy of hearing aids and cochlear implants in children who are hearing-impaired. In: Bess FH, editor. Children with hearing impairment: Contemporary trends. Nashville, TN: Vanderbilt Bill Wilkerson Center Press; 1998. pp. 249–260.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

