Novel avenues of drug discovery and biomarkers for diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 20220043
- PMCID: PMC3033756
- DOI: 10.1177/0091270010362904
Novel avenues of drug discovery and biomarkers for diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Globally, developed nations spend a significant amount of their resources on health care initiatives that poorly translate into increased population life expectancy. As an example, the United States devotes 16% of its gross domestic product to health care, the highest level in the world, but falls behind other nations that enjoy greater individual life expectancy. These observations point to the need for pioneering avenues of drug discovery to increase life span with controlled costs. In particular, innovative drug development for metabolic disorders such as diabetes mellitus becomes increasingly critical given that the number of diabetic people will increase exponentially over the next 20 years. This article discusses the elucidation and targeting of novel cellular pathways that are intimately tied to oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus for new treatment strategies. Pathways that involve wingless, β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD(+)) precursors, and cytokines govern complex biological pathways that determine both cell survival and longevity during diabetes mellitus and its complications. Furthermore, the role of these entities as biomarkers for disease can further enhance their utility irrespective of their treatment potential. Greater understanding of the intricacies of these unique cellular mechanisms will shape future drug discovery for diabetes mellitus to provide focused clinical care with limited or absent long-term complications.
Figures
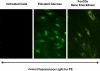
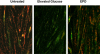
Similar articles
-
Novel directions for diabetes mellitus drug discovery.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2013 Jan;8(1):35-48. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2013.736485. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23092114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of aging and oxidative stress in metabolic and nervous system disorders: programmed cell death and molecular signal transduction crosstalk.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 8;14:1273570. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1273570. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetes mellitus: channeling care through cellular discovery.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2010 Feb;7(1):59-64. doi: 10.2174/156720210790820217. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2010. PMID: 20158461 Free PMC article.
-
Triple play: promoting neurovascular longevity with nicotinamide, WNT, and erythropoietin in diabetes mellitus.Biomed Pharmacother. 2008 Apr-May;62(4):218-32. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2008.01.009. Epub 2008 Feb 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2008. PMID: 18342481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+ ) metabolism in diabetes and diabetic tissues: Implications for nicotinamide-related compound treatment.J Diabetes Investig. 2020 Nov;11(6):1403-1419. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13303. Epub 2020 Jul 7. J Diabetes Investig. 2020. PMID: 32428995 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel directions for diabetes mellitus drug discovery.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2013 Jan;8(1):35-48. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2013.736485. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23092114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol and red wine function as antioxidants in the nervous system without cellular proliferative effects during experimental diabetes.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2010 Nov-Dec;3(6):434-41. doi: 10.4161/oxim.3.6.14741. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2010. PMID: 21307644 Free PMC article.
-
Programming apoptosis and autophagy with novel approaches for diabetes mellitus.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2015;12(2):173-88. doi: 10.2174/1567202612666150305110929. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2015. PMID: 25742566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of aging and oxidative stress in metabolic and nervous system disorders: programmed cell death and molecular signal transduction crosstalk.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 8;14:1273570. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1273570. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT1: new avenues of discovery for disorders of oxidative stress.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012 Feb;16(2):167-78. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2012.648926. Epub 2012 Jan 10. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012. PMID: 22233091 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Development OfEC-oa OECD Health Data 2009. 2009. www.ecosante.org/oecd.htm.
-
- Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, et al. Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. Jama. 2009 May 27;301(20):2129–2140. - PubMed
-
- Rebecchi KR, Wenke JL, Go EP, Desaire H. Label-free quantitation: a new glycoproteomics approach. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2009 Jun;20(6):1048–1059. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

