Transactivation of the dopamine receptor 3 gene by a single provirus integration results in development of B-cell lymphoma in transgenic mice generated from retrovirally transduced embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 20220117
- PMCID: PMC9981455
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-08-240077
Transactivation of the dopamine receptor 3 gene by a single provirus integration results in development of B-cell lymphoma in transgenic mice generated from retrovirally transduced embryonic stem cells
Abstract
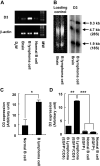
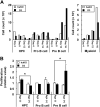
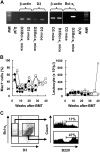
Gene transfer vectors based on retroviruses are commonly used in gene therapy applications because of their unique ability to integrate efficiently into host genomes. This ability also forms the basis of a transformation event that can be induced in transduced cells by transactivation of proto-oncogenes near the vector integration sites. Here, we report on the development of lymphoma in mice generated from embryonic stem cells transduced with an enhanced green fluorescent protein. The cells expressed B220, CD5, Mac1, and IgM on their surfaces and expressed transcription factors characteristic of B-cell lymphoma. Importantly, each mouse had a single copy of the provirus in its genome; the copy was integrated into the second intron of the dopamine receptor 3 (D3) gene, and high-level expression of D3 was detected only in the lymphoma cells. Ectopic expression of D3 in murine marrow cells resulted in preferential proliferation of cells at the pre-B-cell stage in response to a D3-specific agonist, but this proliferation was not observed in vivo. Cells cotransduced with D3 and Bcl-x(L) genes had a phenotype similar to that of lymphoma in vivo, suggesting that the leukemogenesis induced by retroviral integration required "second hit" mutations of additional genes.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Linkage of the potent leukemogenic activity of Meis1 to cell-cycle entry and transcriptional regulation of cyclin D3.Blood. 2010 May 20;115(20):4071-82. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-06-225573. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20237320
-
Aurora kinases A and B are up-regulated by Myc and are essential for maintenance of the malignant state.Blood. 2010 Sep 2;116(9):1498-505. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-251074. Epub 2010 Jun 2. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20519624 Free PMC article.
-
Stable transgene expression in mice generated from retrovirally transduced embryonic stem cells.Mol Ther. 2007 Mar;15(3):560-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.mt.6300063. Epub 2006 Dec 19. Mol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17180117
-
The timing of retroviral silencing correlates with the quality of induced pluripotent stem cell lines.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Feb;1810(2):226-35. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2010.10.004. Epub 2010 Oct 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 20965232
-
Potential use of T cell receptor genes to modify hematopoietic stem cells for the gene therapy of cancer.Pathol Oncol Res. 1999;5(1):3-15. doi: 10.1053/paor.1999.0003. Pathol Oncol Res. 1999. PMID: 10079371 Review.
References
-
- Aiuti A, Cattaneo F, Galimberti S, et al. Gene therapy for immunodeficiency due to adenosine deaminase deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(5):447–458. - PubMed
-
- Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Le Deist F, Carlier F, et al. Sustained correction of X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency by ex vivo gene therapy. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(16):1185–1193. - PubMed
-
- Ott MG, Schmidt M, Schwarzwaelder K, et al. Correction of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease by gene therapy, augmented by insertional activation of MDS1-EVI1, PRDM16 or SETBP1. Nat Med. 2006;12(4):401–409. - PubMed
-
- Cartier N, Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Bartholomae CC, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy with a lentiviral vector in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Science. 2009;326(5954):818–823. - PubMed
-
- Baum C, Düllmann J, Li Z, et al. Side effects of retroviral gene transfer into hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 2003;101(6):2099–2113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

