A novel Wilms tumor 1 (WT1) target gene negatively regulates the WNT signaling pathway
- PMID: 20220130
- PMCID: PMC2863207
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.094334
A novel Wilms tumor 1 (WT1) target gene negatively regulates the WNT signaling pathway
Abstract
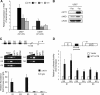
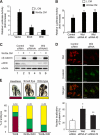
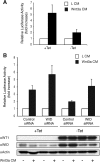
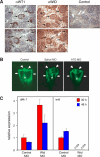
Mammalian kidney development requires the functions of the Wilms tumor gene WT1 and the WNT/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Recent studies have shown that WT1 negatively regulates WNT/beta-catenin signaling, but the molecular mechanisms by which WT1 inhibits WNT/beta-catenin signaling are not completely understood. In this study, we identified a gene, CXXC5, which we have renamed WID (WT1-induced Inhibitor of Dishevelled), as a novel WT1 transcriptional target that negatively regulates WNT/beta-catenin signaling. WT1 activates WID transcription through the upstream enhancer region. In the developing kidney, Wid and Wt1 are coexpressed in podocytes of maturing nephrons. Structure-function analysis demonstrated that WID interacts with Dishevelled via its C-terminal CXXC zinc finger and Dishevelled binding domains and potently inhibits WNT/beta-catenin signaling in vitro and in vivo. WID is evolutionarily conserved, and ablation of wid in zebrafish embryos with antisense morpholino oligonucleotides perturbs embryonic kidney development. Taken together, our results demonstrate that the WT1 negatively regulates WNT/beta-catenin pathway via its target gene WID and further suggest a role for WID in nephrogenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Parathyroid hormone receptor directly interacts with dishevelled to regulate beta-Catenin signaling and osteoclastogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 7;285(19):14756-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.102970. Epub 2010 Mar 8. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20212039 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the beta-catenin signaling pathway by the dishevelled-associated protein Hipk1.PLoS One. 2009;4(2):e4310. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004310. Epub 2009 Feb 2. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19183803 Free PMC article.
-
The KLHL12-Cullin-3 ubiquitin ligase negatively regulates the Wnt-beta-catenin pathway by targeting Dishevelled for degradation.Nat Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;8(4):348-57. doi: 10.1038/ncb1381. Epub 2006 Mar 19. Nat Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16547521
-
New steps in the Wnt/beta-catenin signal transduction pathway.Recent Prog Horm Res. 2000;55:225-36. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2000. PMID: 11036939 Review.
-
Modulation of Wnt signaling by Axin and Axil.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1999 Sep-Dec;10(3-4):255-65. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(99)00017-9. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1999. PMID: 10647780 Review.
Cited by
-
Copy Number Variations Analysis Identifies QPRT as a Candidate Gene Associated With Susceptibility for Solitary Functioning Kidney.Front Genet. 2021 May 17;12:575830. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.575830. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34079576 Free PMC article.
-
Klotho/FGF23 and Wnt Signaling as Important Players in the Comorbidities Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Mar 16;12(3):185. doi: 10.3390/toxins12030185. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32188018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estradiol-Estrogen Receptor α Mediates the Expression of the CXXC5 Gene through the Estrogen Response Element-Dependent Signaling Pathway.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 25;6:37808. doi: 10.1038/srep37808. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27886276 Free PMC article.
-
DNMT3A Haploinsufficiency Transforms FLT3ITD Myeloproliferative Disease into a Rapid, Spontaneous, and Fully Penetrant Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Cancer Discov. 2016 May;6(5):501-15. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0008. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Cancer Discov. 2016. PMID: 27016502 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of WT1 as determinant of heptatocellular carcinoma and its inhibition by Chinese herbal medicine Salvia chinensis Benth and its active ingredient protocatechualdehyde.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 11;8(62):105848-105859. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22406. eCollection 2017 Dec 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29285297 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

