AMP-activated protein kinase antagonizes pro-apoptotic extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation by inducing dual-specificity protein phosphatases in response to glucose deprivation in HCT116 carcinoma
- PMID: 20220132
- PMCID: PMC2863197
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.085456
AMP-activated protein kinase antagonizes pro-apoptotic extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation by inducing dual-specificity protein phosphatases in response to glucose deprivation in HCT116 carcinoma
Erratum in
-
Correction: AMP-activated protein kinase antagonizes pro-apoptotic extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation by inducing dual-specificity protein phosphatases in response to glucose deprivation in HCT116 carcinoma.J Biol Chem. 2018 Nov 16;293(46):18012. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AAC118.006426. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30446602 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
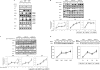
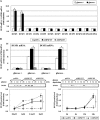
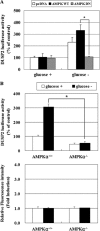
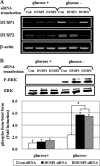
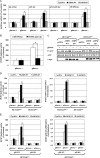
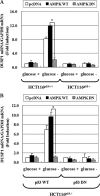
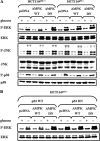
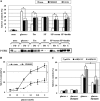
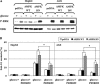
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways are involved in the regulation of cellular responses, including cell proliferation, differentiation, cell growth, and apoptosis. Because these responses are tightly related to cellular energy level, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which plays an essential role in energy homeostasis, has emerged as another key regulator. In the present study, we demonstrate a novel signal network between AMPK and MAPK in HCT116 human colon carcinoma. Glucose deprivation activated AMPK and three MAPK subfamilies, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 MAPK. Under these conditions, inhibition of endogenous AMPK by expressing a dominant-negative form significantly potentiated ERK activation, indicating that glucose deprivation-induced AMPK is specifically antagonizing ERK activity in HCT116 cells. Moreover, we provide novel evidence that AMPK activity is critical for p53-dependent expression of dual-specificity phosphatase (DUSP) 1 & 2, which are negative regulators of ERK. Notably, ERK exhibits pro-apoptotic effects in HCT116 cells under glucose deprivation. Collectively, our data suggest that AMPK protects HCT116 cancer cells from glucose deprivation, in part, via inducing DUSPs, which suppresses pro-apoptotic ERK, further implying that a signal network between AMPK and ERK is a critical regulatory point in coupling the energy status of the cell to the regulation of cell survival.
Figures

References
-
- Hardie D. G., Carling D., Carlson M. (1998) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 821–855 - PubMed
-
- Inoki K., Ouyang H., Zhu T., Lindvall C., Wang Y., Zhang X., Yang Q., Bennett C., Harada Y., Stankunas K., Wang C. Y., He X., MacDougald O. A., You M., Williams B. O., Guan K. L. (2006) Cell 126, 955–968 - PubMed
-
- Jones R. G., Plas D. R., Kubek S., Buzzai M., Mu J., Xu Y., Birnbaum M. J., Thompson C. B. (2005) Mol. Cell 18, 283–293 - PubMed
-
- Xia Z., Dickens M., Raingeaud J., Davis R. J., Greenberg M. E. (1995) Science 270, 1326–1331 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

