Trp-26 imparts functional versatility to human alpha-defensin HNP1
- PMID: 20220136
- PMCID: PMC2871495
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.102749
Trp-26 imparts functional versatility to human alpha-defensin HNP1
Abstract
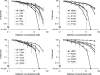
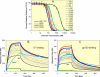
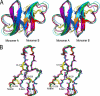
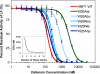
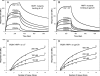
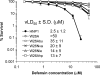
We performed a comprehensive alanine scan of human alpha-defensin HNP1 and tested the ability of the resulting analogs to kill Staphylococcus aureus, inhibit anthrax lethal factor, and bind human immunodeficiency virus-1 gp120. By far, the most deleterious mutation for all of these functions was W26A. The activities lost by W26A-HNP1 were restored progressively by replacing W26 with non-coded, straight-chain aliphatic amino acids of increasing chain length. The hydrophobicity of residue 26 also correlated with the ability of the analogs to bind immobilized wild type HNP1 and to undergo further self-association. Thus, the hydrophobicity of residue 26 is not only a key determinant of the direct interactions of HNP1 with target molecules, but it also governs the ability of this peptide to form dimers and more complex quaternary structures at micromolar concentrations. Although all defensin peptides are cationic, their amphipathicity is at least as important as their positive charge in enabling them to participate in innate host defense.
Figures

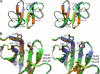

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

