Discovery of potent and selective inhibitors of Trypanosoma brucei ornithine decarboxylase
- PMID: 20220141
- PMCID: PMC2878083
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.081588
Discovery of potent and selective inhibitors of Trypanosoma brucei ornithine decarboxylase
Abstract
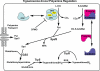
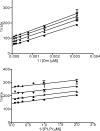
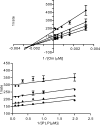
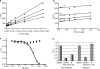
Human African trypanosomiasis, caused by the eukaryotic parasite Trypanosoma brucei, is a serious health problem in much of central Africa. The only validated molecular target for treatment of human African trypanosomiasis is ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), which catalyzes the first step in polyamine metabolism. Here, we describe the use of an enzymatic high throughput screen of 316,114 unique molecules to identify potent and selective inhibitors of ODC. This screen identified four novel families of ODC inhibitors, including the first inhibitors selective for the parasitic enzyme. These compounds display unique binding modes, suggesting the presence of allosteric regulatory sites on the enzyme. Docking of a subset of these inhibitors, coupled with mutagenesis, also supports the existence of these allosteric sites.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (2006) African Trypanosomiasis (Sleeping Sickness), Fact Sheet, 259 Ed., World Health Organization Media Centre, Geneva
-
- Pays E., Nolan D. P. (1998) Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 91, 3–36 - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Monem M. M., Newton N. E., Weeks C. E. (1974) J. Med. Chem. 17, 447–451 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

