Induction of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin expression by co-stimulation with interleukin-17 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha is controlled by IkappaB-zeta but neither by C/EBP-beta nor C/EBP-delta
- PMID: 20220144
- PMCID: PMC2863242
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.017129
Induction of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin expression by co-stimulation with interleukin-17 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha is controlled by IkappaB-zeta but neither by C/EBP-beta nor C/EBP-delta
Abstract
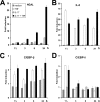
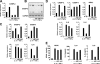
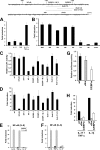
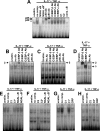
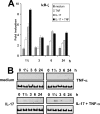
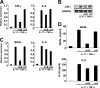
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) is a siderophore-binding antimicrobial protein that is up-regulated in epithelial tissues during inflammation. We demonstrated previously that the gene encoding NGAL (LCN2) is strongly up-regulated by interleukin (IL)-1beta in an NF-kappaB-dependent manner but not by tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, another potent activator of NF-kappaB. This is due to an IL-1beta-specific synthesis of the NF-kappaB-binding co-factor IkappaB-zeta, which is essential for NGAL induction. We demonstrate here that NGAL is strongly induced by stimulation with TNF-alpha in the presence of IL-17, a pro-inflammatory cytokine produced by the newly discovered subset of CD4(+) T helper cells, T(H)-17. In contrast to the murine NGAL orthologue, 24p3/lipocalin 2, we found no requirement for C/EBP-beta or C/EBP-delta for NGAL induction by IL-17 and TNF-alpha as neither small interfering RNAs against the two C/EBP mRNAs nor mutation of the C/EBP sites in the LCN2 promoter abolished IL-17- and TNF-alpha-induced up-regulation of NGAL. NGAL induction is governed solely by NF-kappaB and its co-factor IkappaB-zeta. This was demonstrated by a pronounced reduction in the amount of NGAL mRNA and NGAL protein synthesized in cells treated with small interfering RNA against IkappaB-zeta and a total lack of activation of an LCN2 promoter construct with a mutated NF-kappaB site. As IL-17 stimulation stabilizes the IkappaB-zeta transcript, we propose a model where TNF-alpha induces activation and binding of NF-kappaB to the promoters of both NFKBIZ and LCN2 genes but induce only transcription of IkappaB-zeta. Co-stimulation with IL-17 leads to accumulation of IkappaB-zeta mRNA and IkappaB-zeta protein, which can bind to NF-kappaB on the LCN2 promoter and thus induce NGAL expression.
Figures

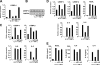
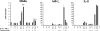
Similar articles
-
Crucial roles of binding sites for NF-kappaB and C/EBPs in IkappaB-zeta-mediated transcriptional activation.Biochem J. 2007 Aug 1;405(3):605-15. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061797. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17447895 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1beta-specific up-regulation of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is controlled by IkappaB-zeta.J Immunol. 2006 May 1;176(9):5559-66. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.9.5559. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16622025
-
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is up-regulated in human epithelial cells by IL-1 beta, but not by TNF-alpha.J Immunol. 2003 Dec 15;171(12):6630-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.12.6630. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14662866
-
The multifaceted roles of neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) in inflammation and cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Aug;1826(1):129-69. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.03.008. Epub 2012 Mar 31. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22513004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin--an emerging troponin for kidney injury.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008 Dec;23(12):3737-43. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn531. Epub 2008 Sep 22. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008. PMID: 18809975 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Serum and Urine Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Levels Measured at Admission Predict Progression to Chronic Kidney Disease in Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury Patients.Dis Markers. 2020 Aug 17;2020:8883404. doi: 10.1155/2020/8883404. eCollection 2020. Dis Markers. 2020. PMID: 32908617 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Ameliorates Zymosan-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in BALB/c Mice.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 14;8(1):16814. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35254-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30429582 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting soluble tumor necrosis factor as a potential intervention to lower risk for late-onset Alzheimer's disease associated with obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019 Dec 31;12(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0546-4. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31892368 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-17-induced protein lipocalin 2 is dispensable for immunity to oral candidiasis.Infect Immun. 2014 Mar;82(3):1030-5. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01389-13. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24343647 Free PMC article.
-
Lipocalin 2 expression and secretion is highly regulated by metabolic stress, cytokines, and nutrients in adipocytes.PLoS One. 2014 May 12;9(5):e96997. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096997. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24818605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cowland J. B., Sørensen O. E., Sehested M., Borregaard N. (2003) J. Immunol. 171, 6630–6639 - PubMed
-
- Sørensen O. E., Cowland J. B., Theilgaard-Mönch K., Liu L., Ganz T., Borregaard N. (2003) J. Immunol. 170, 5583–5589 - PubMed
-
- Sørensen O. E., Thapa D. R., Rosenthal A., Liu L., Roberts A. A., Ganz T. (2005) J. Immunol. 174, 4870–4879 - PubMed
-
- Kao C. Y., Chen Y., Thai P., Wachi S., Huang F., Kim C., Harper R. W., Wu R. (2004) J. Immunol. 173, 3482–3491 - PubMed
-
- Kjeldsen L., Bainton D. F., Sengeløv H., Borregaard N. (1994) Blood 83, 799–807 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

