Inter- and intraobserver variation between radiologists in the detection of abnormal parenchymal lung changes on high-resolution computed tomography
- PMID: 20220262
- PMCID: PMC2855063
- DOI: 10.4103/0256-4947.60518
Inter- and intraobserver variation between radiologists in the detection of abnormal parenchymal lung changes on high-resolution computed tomography
Abstract
Background and objectives: Radiological and histological evaluations are affected by subjective interpretation. This study determined the level of inter- and intraobserver variation among radiologists for detection of abnormal parenchymal lung changes on high resolution computed tomography (HRCT).
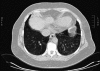
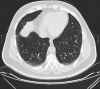
Methods: HRCT images of 65 patients known to have systemic lupus erythematosus (with clinical pulmonary involvement) were retrospectively reviewed by four nonthoracic radiologists (two with expertise in magnetic resonance [MR] and two general radiologists). Each radiologist read the scans twice, with an interval between readings of at least 6 months. The interobserver variation among the first and second readings of the four radiologists and the intraobserver variation of each radiologist's two readings were assessed by the kappa statistic.
Results: There was good agreement between the first and second readings of each radiologist. There was moderate agreement between the two readings of one MR radiologist (kappa=0.482); the other three radiologists had kappa values that were good to excellent (0.716, 0.691, and 0.829). There was a clinically acceptable level of interobserver variability between all radiologists. The agreement was fair to moderate between the MR radiologist and the other observers (kappa range: 0.362-0.519) and moderate to good between the other three radiologists (0.508-0.730).
Conclusion: The interpretation of imaging findings of abnormal parenchymal lung changes on HRCT is reproducible and the agreement between general radiologists is clinically acceptable. There is reduced agreement when the radiologist is not involved on a regular basis with thoracic imaging. Difficult or indeterminate cases may benefit from review by a chest radiologist.
Figures
References
-
- Carrington CB, Gaensler EA, Coutu RE, FitzGerald MX, Gupta RG. Natural history and treated course of usual and desquamative interstitial pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1978;298:801–9. - PubMed
-
- Wright PH, Heard BE, Steel SJ, Turner-Warwick M. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis: Assessment by graded trephine lung biopsy histology compared with clinical, radiographic and physiological features. Br J Dis Chest. 1981;75:61–70. - PubMed
-
- Panos RJ, Mortenson RL, Niccoli SA, King TE., Jr Clinical deterioration in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: causes and assessment. Am J Med. 1990;88:396–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

