Transcriptome genetics using second generation sequencing in a Caucasian population
- PMID: 20220756
- PMCID: PMC3836232
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08903
Transcriptome genetics using second generation sequencing in a Caucasian population
Abstract
Gene expression is an important phenotype that informs about genetic and environmental effects on cellular state. Many studies have previously identified genetic variants for gene expression phenotypes using custom and commercially available microarrays. Second generation sequencing technologies are now providing unprecedented access to the fine structure of the transcriptome. We have sequenced the mRNA fraction of the transcriptome in 60 extended HapMap individuals of European descent and have combined these data with genetic variants from the HapMap3 project. We have quantified exon abundance based on read depth and have also developed methods to quantify whole transcript abundance. We have found that approximately 10 million reads of sequencing can provide access to the same dynamic range as arrays with better quantification of alternative and highly abundant transcripts. Correlation with SNPs (small nucleotide polymorphisms) leads to a larger discovery of eQTLs (expression quantitative trait loci) than with arrays. We also detect a substantial number of variants that influence the structure of mature transcripts indicating variants responsible for alternative splicing. Finally, measures of allele-specific expression allowed the identification of rare eQTLs and allelic differences in transcript structure. This analysis shows that high throughput sequencing technologies reveal new properties of genetic effects on the transcriptome and allow the exploration of genetic effects in cellular processes.
Figures
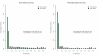
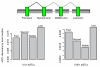

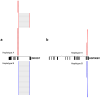
References
-
- Emilsson V, et al. Genetics of gene expression and its effect on disease. Nature. 2008;452:423–8. - PubMed
-
- Goring HH, et al. Discovery of expression QTLs using large-scale transcriptional profiling in human lymphocytes. Nat Genet. 2007;39:1208–16. - PubMed
-
- Moffatt MF, et al. Genetic variants regulating ORMDL3 expression contribute to the risk of childhood asthma. Nature. 2007;448:470–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

