Understanding mechanisms underlying human gene expression variation with RNA sequencing
- PMID: 20220758
- PMCID: PMC3089435
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08872
Understanding mechanisms underlying human gene expression variation with RNA sequencing
Abstract
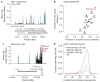
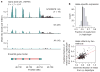
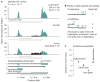
Understanding the genetic mechanisms underlying natural variation in gene expression is a central goal of both medical and evolutionary genetics, and studies of expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) have become an important tool for achieving this goal. Although all eQTL studies so far have assayed messenger RNA levels using expression microarrays, recent advances in RNA sequencing enable the analysis of transcript variation at unprecedented resolution. We sequenced RNA from 69 lymphoblastoid cell lines derived from unrelated Nigerian individuals that have been extensively genotyped by the International HapMap Project. By pooling data from all individuals, we generated a map of the transcriptional landscape of these cells, identifying extensive use of unannotated untranslated regions and more than 100 new putative protein-coding exons. Using the genotypes from the HapMap project, we identified more than a thousand genes at which genetic variation influences overall expression levels or splicing. We demonstrate that eQTLs near genes generally act by a mechanism involving allele-specific expression, and that variation that influences the inclusion of an exon is enriched within and near the consensus splice sites. Our results illustrate the power of high-throughput sequencing for the joint analysis of variation in transcription, splicing and allele-specific expression across individuals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

