Deep brain stimulation for psychiatric disorders
- PMID: 20221269
- PMCID: PMC2835924
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2010.0105
Deep brain stimulation for psychiatric disorders
Abstract
Background: Deep brain stimulation (DBS), an established treatment for some movement disorders, is now being used experimentally to treat psychiatric disorders as well. In a number of recently published case series, DBS yielded an impressive therapeutic benefit in patients with medically intractable psychiatric diseases.
Methods: This review of the use of DBS to treat psychiatric disorders is based on literature retrieved from a selective Pubmed search for relevant keywords, reference works on the topic, and the authors' own research.
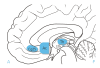
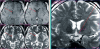
Results: Studies have been performed on the use of DBS to treat medically intractable obsessive-compulsive disorder, depressive disorders, and Tourette syndrome. The case numbers in the cited publications were small, yet at least some of them involved a methodologically sound investigation. Thus, in some studies, the strength of the effect was controlled with a double-blinded interval in which the stimulation was turned off. In general, the primary symptoms were found to improve markedly, by 35% to 70%, although not all patients responded to the treatment. Adverse effects of DBS were very rare in most studies and could usually be reversed by changing the stimulation parameters.
Conclusions: The results of DBS for psychiatric disorders that have been published to date are encouraging. They open up a new perspective in the treatment of otherwise intractable disorders. Nonetheless, the efficacy, mechanism of action, and adverse effects of DBS for this indication still need to be further studied in methodologically adequate trials that meet the highest ethical standard.
Figures
Comment in
-
Careful research needed: The use of deep brain stimulation in psychiatric illnesses.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2010 Feb;107(7):103-4. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2010.0103. Epub 2010 Feb 19. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2010. PMID: 20221268 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Re: Deep brain stimulation for psychiatric disorders. Additional reference.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2010 Sep;107(37):644; author reply 645-6. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2010.0644a. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2010. PMID: 20959892 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Re: Deep brain stimulation for psychiatric disorders. Topic for ethics committee.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2010 Sep;107(37):644; author reply 645-6. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2010.0644b. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2010. PMID: 20959893 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Re: Deep brain stimulation for psychiatric disorders. A new opportunity.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2010 Sep;107(37):645; author reply 645-6. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2010.0645a. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2010. PMID: 20959894 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Nuttin BJ, Gabriels LA, Cosyns PR, et al. Long-term electrical capsular stimulation in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neurosurgery. 2003;52:1263–1272. discussion 1272-4. - PubMed
-
- Abelson JL., Curtis G, Sagher O, et al. Deep brain stimulation for refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;57:510–516. - PubMed
-
- Mallet L, Polosan M, Jaafari N, et al. Subthalamic nucleus stimulation in severe obsessive-compulsive disorder. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2121–2134. - PubMed
-
- Gabriels L, Cosyns P, Nuttin B, Demeulemeester H, Gybels J. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: psychopathological and neuropsychological outcome in three cases. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 2003;107:275–282. - PubMed
-
- Nuttin B, Cosyns P, Demeulemeester H, Gybels J, Meyerson B. Electrical stimulation in anterior limbs of internal capsules in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Lancet. 1999;354 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

