MLCK and PKC Involvements via Gi and Rho A Protein in Contraction by the Electrical Field Stimulation in Feline Esophageal Smooth Muscle
- PMID: 20221277
- PMCID: PMC2835980
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.1.29
MLCK and PKC Involvements via Gi and Rho A Protein in Contraction by the Electrical Field Stimulation in Feline Esophageal Smooth Muscle
Abstract
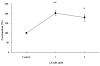
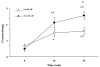
We have shown that myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) was required for the off-contraction in response to the electrical field stimulation (EFS) of feline esophageal smooth muscle. In this study, we investigated whether protein kinase C (PKC) may require the on-contraction in response to EFS using feline esophageal smooth muscle. The contractions were recorded using an isometric force transducer. On-contraction occurred in the presence of N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), suggesting that nitric oxide acts as an inhibitory mediator in smooth muscle. The excitatory composition of both contractions was cholinergic dependent which was blocked by tetrodotoxin or atropine. The on-contraction was abolished in Ca(2+)-free buffer but reappeared in normal Ca(2+)-containing buffer indicating that the contraction was Ca(2+) dependent. 4-aminopyridine (4-AP), voltage-dependent K(+) channel blocker, significantly enhanced on-contraction. Aluminum fluoride (a G-protein activator) increased on-contraction. Pertussis toxin (a G(i) inactivator) and C3 exoenzyme (a rhoA inactivator) significantly decreased on-contraction suggesting that Gi or rhoA protein may be related with Ca(2+) and K(+) channel. ML-9, a MLCK inhibitor, significantly inhibited on-contraction, and chelerythrine (PKC inhibitor) affected on the contraction. These results suggest that endogenous cholinergic contractions activated directly by low-frequency EFS may be mediated by Ca(2+), and G proteins, such as Gi and rhoA, which resulted in the activation of MLCK, and PKC to produce the contraction in feline distal esophageal smooth muscle.
Keywords: Ca2+; Electrical field stimulation; Esophagus; G protein; K+; On contraction; Smooth muscle.
Figures
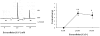
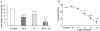
References
-
- Conklin JL. Nitric oxide: a mediator of esophageal motor function. J Lab Clin Med. 1998;131:10–20. - PubMed
-
- Preiksaitis HG, Tremblay L, Diamant NE. Nitric oxide mediates inhibitory nerve effects in human esophagus and lower esophageal sphincter. Dig Dis Sci. 1994;39:770–775. - PubMed
-
- Richards WG, Sugarbaker DJ. Neuronal control of esophageal function. Chest Surg Clin N Am. 1995;5:157–171. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert RJ, Dodds WJ. Effect of selective muscarinic antagonists on peristaltic contractions in opossum smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1986;250:G50–G59. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

