R-type Calcium Channel Isoform in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons
- PMID: 20221279
- PMCID: PMC2835982
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.1.45
R-type Calcium Channel Isoform in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons
Abstract
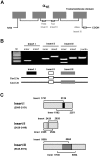
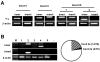
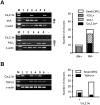
R-type Ca(v)2.3 high voltage-activated Ca(2+) channels in peripheral sensory neurons contribute to pain transmission. Recently we have demonstrated that, among the six Ca(v)2.3 isoforms (Ca(v)2.3a~Ca(v)2.3e), the Ca(v)2.3e isoform is primarily expressed in trigeminal ganglion (TG) nociceptive neurons. In the present study, we further investigated expression patterns of Ca(v)2.3 isoforms in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. As in TG neurons, whole tissue RT-PCR analyses revealed the presence of two isoforms, Ca(v)2.3a and Ca(v)2.3e, in DRG neurons. Single-cell RT-PCR detected the expression of Ca(v)2.3e mRNA in 20% (n=14/70) of DRG neurons, relative to Ca(v)2.3a expression in 2.8% (n=2/70) of DRG neurons. Ca(v)2.3e mRNA was mainly detected in small-sized neurons (n=12/14), but in only a few medium-sized neurons (n=2/14) and not in large-sized neurons, indicating the prominence of Ca(v)2.3e in nociceptive DRG neurons. Moreover, Ca(v)2.3e was preferentially expressed in tyrosine-kinase A (trkA)-positive, isolectin B4 (IB4)-negative and transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1)-positive neurons. These results suggest that Ca(v)2.3e may be the main R-type Ca(2+) channel isoform in nociceptive DRG neurons and thereby a potential target for pain treatment, not only in the trigeminal system but also in the spinal system.
Keywords: Cav2.3; DRG neurons; R-type calcium channels; Voltage-activated calcium channels.
Figures
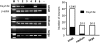
Similar articles
-
Molecular basis of Ca(v)2.3 calcium channels in rat nociceptive neurons.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 16;282(7):4757-4764. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605248200. Epub 2006 Dec 4. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17145762 Free PMC article.
-
High voltage-activated Ca(2+) channel currents in isolectin B(4)-positive and -negative small dorsal root ganglion neurons of rats.Neurosci Lett. 2004 Sep 16;368(1):96-101. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2004.06.067. Neurosci Lett. 2004. PMID: 15342142
-
Involvement of hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channels in dorsal root ganglion in neuropathic pain.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008 Oct 25;60(5):579-80. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18958363
-
Expression and Regulation of Cav3.2 T-Type Calcium Channels during Inflammatory Hyperalgesia in Mouse Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons.PLoS One. 2015 May 14;10(5):e0127572. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127572. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25974104 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling mechanisms of down-regulation of voltage-activated Ca2+ channels by transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 stimulation with olvanil in primary sensory neurons.Neuroscience. 2006 Aug 11;141(1):407-19. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.03.023. Epub 2006 May 6. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16678970
Cited by
-
Animal Venom Peptides Cause Antinociceptive Effects by Voltage-gated Calcium Channels Activity Blockage.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(8):1579-1599. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210713121217. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34259147 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Cav2.1 and Cav2.3 channel inhibition by baclofen and α-conotoxin Vc1.1 via GABAB receptor activation.J Gen Physiol. 2014 Apr;143(4):465-79. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201311104. J Gen Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24688019 Free PMC article.
-
A previously unrecognized superfamily of macro-conotoxins includes an inhibitor of the sensory neuron calcium channel Cav2.3.PLoS Biol. 2023 Aug 3;21(8):e3002217. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002217. eCollection 2023 Aug. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37535677 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Inhibition of Voltage-gated Ca(2+) Channels for Chronic Pain Relief.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2013 Dec;11(6):606-20. doi: 10.2174/1570159X11311060005. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24396337 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative RNA splicing: contribution to pain and potential therapeutic strategy.Drug Discov Today. 2016 Nov;21(11):1787-1798. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2016.06.017. Epub 2016 Jun 18. Drug Discov Today. 2016. PMID: 27329269 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vanegas H, Schaible H. Effects of antagonists to high-threshold calcium channels upon spinal mechanisms of pain, hyperalgesia and allodynia. Pain. 2000;85:9–18. - PubMed
-
- Ikeda M, Matsumoto S. Classification of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in trigeminal ganglion neurons from neonatal rats. Life Sci. 2003;73:1175–1187. - PubMed
-
- Williams ME, Feldman DH, McCue AF, Brenner R, Velicelebi G, Ellis SB, Harpold MM. Structure and functional expression of alpha 1, alpha 2, and beta subunits of a novel human neuronal calcium channel subtype. Neuron. 1992;8:71–84. - PubMed
-
- Bourinet E, Soong TW, Sutton K, Slaymaker S, Mathews E, Monteil A, Zamponi GW, Nargeot J, Snutch TP. Splicing of alpha 1A subunit gene generates phenotypic variants of P- and Q-type calcium channels. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:407–415. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

