The role of parents and family members in ART treatment adherence: Evidence from Thailand
- PMID: 20221313
- PMCID: PMC2835367
- DOI: 10.1177/0164027509348130
The role of parents and family members in ART treatment adherence: Evidence from Thailand
Abstract
High levels of treatment adherence are crucial for the success of expanding ART treatment programs everywhere. Augmenting adherence through treatment supporters is one promising strategy. Most discussions focus on peers, especially members of PHA groups, for this purpose. Far less attention is given to family members and especially older age parents. Yet ART recipients often live with or nearby parents and other family members who are highly motivated to ensure the treatment's success. This study examines the extent that family members, especially parents, assist adherence in Thailand. Results indicate that most adult ART patients live with family members and over half live with or in the same locality as a parent. Family members, including parents, commonly remind ART patients to take medications, especially if coresident. Moreover, parents often remind patients to get resupplies and sometimes accompany them to appointments. Clearly close family members, including parents, should be explicitly incorporated into adherence augmentation programs and provided adequate information to facilitate their role as long-term adherence partners, not only in Thailand but wherever ART recipients are closely linked to family members through living and caregiving arrangements.
Figures
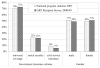
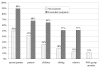
Similar articles
-
Parents and family members in the era of ART: evidence from Cambodia and Thailand.AIDS Care. 2011 Oct;23(10):1264-73. doi: 10.1080/09540121.2011.555741. Epub 2011 Jul 5. AIDS Care. 2011. PMID: 21726159 Free PMC article.
-
Overlooked potential: older-age parents in the era of ART.AIDS Care. 2008 Nov;20(10):1169-76. doi: 10.1080/09540120701854642. AIDS Care. 2008. PMID: 19012079
-
"How am I going to live?": exploring barriers to ART adherence among adolescents and young adults living with HIV in Uganda.BMC Public Health. 2018 Oct 4;18(1):1158. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-6048-7. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30286746 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dementia -- Caring, Ethics, Ethnical and Economical Aspects: A Systematic Review [Internet].Stockholm: Swedish Council on Health Technology Assessment (SBU); 2008 Jun. SBU Assessment No. 172. Stockholm: Swedish Council on Health Technology Assessment (SBU); 2008 Jun. SBU Assessment No. 172. PMID: 28876770 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Improving Communication about Care Goals for Children with ADHD [Internet].Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2020 Nov. Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2020 Nov. PMID: 37607239 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Barriers and facilitators to antiretroviral adherence and retention in HIV care among people living with HIV in the Comarca Ngäbe-Buglé, Panama.PLoS One. 2022 Jun 16;17(6):e0270044. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270044. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35709223 Free PMC article.
-
On the road to HIV/AIDS competence in the household: building a health-enabling environment for people living with HIV/AIDS.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015 Mar 18;12(3):3264-92. doi: 10.3390/ijerph120303264. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015. PMID: 25794189 Free PMC article.
-
HIV/AIDS and older adults in Cameroon: Emerging issues and implications for caregiving and policy-making.SAHARA J. 2018 Dec;15(1):7-19. doi: 10.1080/17290376.2018.1433059. SAHARA J. 2018. PMID: 29409392 Free PMC article.
-
A Qualitative Exploration of Psychosocial Challenges of Perinatally HIV-Infected Adolescents and Families in Bangkok, Thailand.Vulnerable Child Youth Stud. 2018;13(2):158-169. doi: 10.1080/17450128.2017.1356947. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Vulnerable Child Youth Stud. 2018. PMID: 30344614 Free PMC article.
-
Density of healthcare providers and patient outcomes: evidence from a nationally representative multi-site HIV treatment program in Uganda.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 17;6(1):e16279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016279. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21264224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews Frank, et al. Multiple Classification Analysis: A Report on a Computer Program for Multiple Regression Using Categorical Predictors. 2nd. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan, Institute for Social Research; 1973.
-
- Beals KP, Wight RG, Aneshensel CS, Murphy DA, Miller-Martinez D. The role of family caregivers in HIV medication adherence. AIDS CARE. 2006;18(6):589–596. - PubMed
-
- Burrage Joe, Demi Alice. Buddy Programs for People Infected With HIV. Journal of the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care. 2003;14(1):52–62. - PubMed
-
- Chayovan Napaporn. Health and Population Studies Based On the 1987 Thailand Demographic and Health Survey Demographic and Health Surveys Further Analysis Series, No 1. New York: Population Council and Institute for Resource Development; 1989. Marriage registration among Thai women.
-
- Hope R, Israel E. The essentials of antiretroviral therapy for health care and program managers Pathfinder International, Technical Guidance Series Number 5. Watertown MA: Pathfinder International; 2007.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

