Damage of guinea pig heart and arteries by a trioleate-enriched diet and of cultured cardiomyocytes by oleic acid
- PMID: 20221399
- PMCID: PMC2833202
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009561
Damage of guinea pig heart and arteries by a trioleate-enriched diet and of cultured cardiomyocytes by oleic acid
Abstract
Background: Mono-unsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) like oleic acid have been shown to cause apoptosis of cultured endothelial cells by activating protein phosphatase type 2C alpha and beta (PP2C). The question arises whether damage of endothelial or other cells could be observed in intact animals fed with a trioleate-enriched diet.
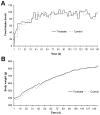
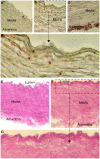
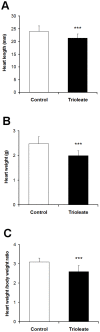
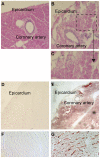
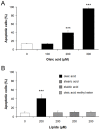
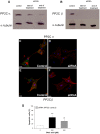
Methodology/principal findings: Dunkin-Hartley guinea pigs were fed with a trioleate-enriched diet for 5 months. Advanced atherosclerotic changes of the aorta and the coronary arteries could not be seen but the arteries appeared in a pre-atherosclerotic stage of vascular remodelling. However, the weight and size of the hearts were lower than in controls and the number of apoptotic myocytes increased in the hearts of trioleate-fed animals. To confirm the idea that oleic acid may have caused this apoptosis by activation of PP2C, cultured cardiomyocytes from guinea pigs and mice were treated with various lipids. It was demonstrable that oleic acid dose-dependently caused apoptosis of cardiomyocytes from both species, yet, similar to previous experiments with cultured neurons and endothelial cells, stearic acid, elaidic acid and oleic acid methylester did not. The apoptotic effect caused by oleic acid was diminished when PP2C alpha and beta were downregulated by siRNA showing that PP2C was causally involved in apoptosis caused by oleic acid.
Conclusions/significance: The glycerol trioleate diet given to guinea pigs for 5 months did not cause marked atherosclerosis but clearly damaged the hearts by activating PP2C alpha and beta. The diet used with 24% (wt/wt) glycerol trioleate is not comparable to human diets. The detrimental role of MUFAs for guinea pig heart tissue in vivo is shown for the first time. Whether it is true for humans remains to be shown.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Klumpp S, Selke D, Hermesmeier J. Protein phosphatase type 2C active at physiological Mg2+: stimulation by unsaturated fatty acids. FEBS Lett. 1998;437:229–232. - PubMed
-
- Klumpp S, Selke D, Ahlemeyer B, Schaper C, Krieglstein J. Relationship between protein phosphatase type 2C activity and induction of apoptosis in cultured neuronal cells. Neurochem Int. 2002;41:251–259. - PubMed
-
- Hufnagel B, Dworak M, Soufi M, Mester Z, Zhu Y, et al. Unsaturated fatty acids isolated from human lipoproteins activate protein phospatase type 2Cβ and induce apoptosis in endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 2005;180:245–254. - PubMed
-
- Schwarz S, Hufnagel B, Dworak M, Klumpp S, Krieglstein J. Protein phosphatase type 2Cα and 2Cβ are involved in fatty-acid-induced apoptosis of neuronal and endothelial cells. Apoptosis. 2006;11:1111–1119. - PubMed
-
- Klumpp S, Thissen MC, Krieglstein J. Protein phosphatases types 2Cα and 2Cβ in apoptosis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006;34:1370–1375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

