The type 1 diabetes - HLA susceptibility interactome--identification of HLA genotype-specific disease genes for type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 20221424
- PMCID: PMC2832689
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009576
The type 1 diabetes - HLA susceptibility interactome--identification of HLA genotype-specific disease genes for type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Background: The individual contribution of genes in the HLA region to the risk of developing type 1 diabetes (T1D) is confounded by the high linkage disequilibrium (LD) in this region. Using a novel approach we have combined genetic association data with information on functional protein-protein interactions to elucidate risk independent of LD and to place the genetic association into a functional context.
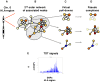
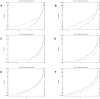
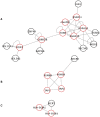
Methodology/principal findings: Genetic association data from 2300 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the HLA region was analysed in 2200 T1D family trios divided into six risk groups based on HLA-DRB1 genotypes. The best SNP signal in each gene was mapped to proteins in a human protein interaction network and their significance of clustering in functional network modules was evaluated. The significant network modules identified through this approach differed between the six HLA risk groups, which could be divided into two groups based on carrying the DRB1*0301 or the DRB1*0401 allele. Proteins identified in networks specific for DRB1*0301 carriers were involved in stress response and inflammation whereas in DRB1*0401 carriers the proteins were involved in antigen processing and presentation.
Conclusions/significance: In this study we were able to hypothesise functional differences between individuals with T1D carrying specific DRB1 alleles. The results point at candidate proteins involved in distinct cellular processes that could not only help the understanding of the pathogenesis of T1D, but also the distinction between individuals at different genetic risk for developing T1D.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Several loci in the HLA class III region are associated with T1D risk after adjusting for DRB1-DQB1.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009 Feb;11 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):46-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2008.01002.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009. PMID: 19143814 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms in the genes encoding TGF-beta1, TNF-alpha, and IL-6 show association with type 1 diabetes mellitus in the Slovak population.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2010 Oct;58(5):385-93. doi: 10.1007/s00005-010-0092-z. Epub 2010 Aug 5. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2010. PMID: 20686866
-
Contribution of selective HLA-DRB1/DQB1 alleles and haplotypes to the genetic susceptibility of type 1 diabetes among Lebanese and Bahraini Arabs.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005 Sep;90(9):5104-9. doi: 10.1210/jc.2005-1166. Epub 2005 Jun 28. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005. PMID: 15985473
-
HLA and autoimmune diseases: Type 1 diabetes (T1D) as an example.Autoimmun Rev. 2006 Mar;5(3):187-94. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2005.06.002. Epub 2005 Aug 1. Autoimmun Rev. 2006. PMID: 16483918 Review.
-
Pro-inflammatory variants of DRB1 and RAGE genes are associated with susceptibility to pediatric type 1 diabetes: a new hypothesis on the adaptive role of autoimmunity.Riv Biol. 2007 May-Aug;100(2):285-304. Riv Biol. 2007. PMID: 17987563 Review.
Cited by
-
Benchmarking the HLA typing performance of Polysolver and Optitype in 50 Danish parental trios.BMC Bioinformatics. 2018 Jun 25;19(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2239-6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29940840 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel type 1 diabetes candidate genes by integrating genome-wide association data, protein-protein interactions, and human pancreatic islet gene expression.Diabetes. 2012 Apr;61(4):954-62. doi: 10.2337/db11-1263. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22344559 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of type 1 diabetes.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012 Jan;2(1):a007732. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a007732. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012. PMID: 22315720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zonulin, regulation of tight junctions, and autoimmune diseases.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012 Jul;1258(1):25-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06538.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012. PMID: 22731712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical features, biochemistry and HLA-DRB1 status in children and adolescents with diabetes in Dhaka, Bangladesh.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019 Dec;158:107894. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107894. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019. PMID: 31669629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nerup J, Platz P, Andersen OO, Christy M, Lyngsoe J, et al. HL-A antigens and diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1974;2:864–866. - PubMed
-
- She JX. Susceptibility to type I diabetes: HLA-DQ and DR revisited. Immunol Today. 1996;17:323–329. - PubMed
-
- Pociot F, McDermott MF. Genetics of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Genes Immun. 2002;3:235–249. - PubMed
-
- Cucca F, Lampis R, Congia M, Angius E, Nutland S, et al. A correlation between the relative predisposition of MHC class II alleles to type 1 diabetes and the structure of their proteins. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10:2025–2037. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

